Transgenerational effects of environmental enrichment on repetitive motor behavior development
- PMID: 27059336
- PMCID: PMC4853249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.04.005
Transgenerational effects of environmental enrichment on repetitive motor behavior development
Abstract
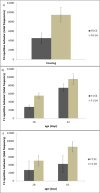
The favorable consequences of environmental enrichment (EE) on brain and behavior development are well documented. Much less is known, however, about transgenerational benefits of EE on non-enriched offspring. We explored whether transgenerational effects of EE might extend to the development of repetitive motor behaviors in deer mice. Repetitive motor behaviors are invariant patterns of movement that, across species, can be reduced by EE. We found that EE not only attenuated the development of repetitive behavior in dams, but also in their non-enriched offspring. Moreover, maternal behavior did not seem to mediate the transgenerational effect we found, although repetitive behavior was affected by reproductive experience. These data support a beneficial transgenerational effect of EE on repetitive behavior development and suggest a novel benefit of reproductive experience.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder; Deer mice; Early experience; Maternal behavior; Reproductive experience.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
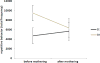
Similar articles
-
The development of repetitive motor behaviors in deer mice: Effects of environmental enrichment, repeated testing, and differential mediation by indirect basal ganglia pathway activation.Dev Psychobiol. 2017 Apr;59(3):390-399. doi: 10.1002/dev.21503. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Dev Psychobiol. 2017. PMID: 28181216 Free PMC article.
-
How does environmental enrichment reduce repetitive motor behaviors? Neuronal activation and dendritic morphology in the indirect basal ganglia pathway of a mouse model.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Feb 15;299:122-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.11.029. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26620495 Free PMC article.
-
Development of spontaneous stereotyped behavior in deer mice: effects of early and late exposure to a more complex environment.Dev Psychobiol. 2000 Sep;37(2):100-8. Dev Psychobiol. 2000. PMID: 10954835
-
Animal models of restricted repetitive behavior in autism.Behav Brain Res. 2007 Jan 10;176(1):66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.08.023. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Behav Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 16997392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction of restricted repetitive behavior by environmental enrichment: Potential neurobiological mechanisms.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023 Sep;152:105291. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105291. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023. PMID: 37353046 Review.
Cited by
-
Environmental Enrichment During Adulthood Reduces Sucrose Binge-Like Intake in a High Drinking in the Dark Phenotype (HD) in C57BL/6J Mice.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Feb 15;13:27. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00027. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30828291 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental Enrichment Modulates Drug Addiction and Binge-Like Consumption of Highly Rewarding Substances: A Role for Anxiety and Compulsivity Brain Systems?Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Nov 29;12:295. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00295. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30555310 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental Enrichment During Adolescence Acts as a Protective and Therapeutic Tool for Ethanol Binge-Drinking, Anxiety-Like, Novelty Seeking and Compulsive-Like Behaviors in C57BL/6J Mice During Adulthood.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Aug 20;12:177. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00177. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30177875 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-reproductive Parental Enriching Experiences Influence Progeny's Developmental Trajectories.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Nov 12;12:254. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00254. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30483072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cutuli D, Caporali P, Gelfo F, Angelucci F, Laricchiuta D, Foti F, Bartolo PDe, Bisicchia E, Molinari M, Vecchioli SFarioli, Petrosini L. Pre-reproductive maternal enrichment influences rat maternal care and offspring developmental trajectories: behavioral performances and neuroplasticity correlates, Front. Behav Neurosci. 2015;9:66. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Denenberg VH, Rosenberg KM. Nongenetic transmission of information. Nature. 1967;216:549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

