Transgenerational effects of environmental enrichment on repetitive motor behavior development
- PMID: 27059336
- PMCID: PMC4853249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.04.005
Transgenerational effects of environmental enrichment on repetitive motor behavior development
Abstract
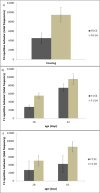
The favorable consequences of environmental enrichment (EE) on brain and behavior development are well documented. Much less is known, however, about transgenerational benefits of EE on non-enriched offspring. We explored whether transgenerational effects of EE might extend to the development of repetitive motor behaviors in deer mice. Repetitive motor behaviors are invariant patterns of movement that, across species, can be reduced by EE. We found that EE not only attenuated the development of repetitive behavior in dams, but also in their non-enriched offspring. Moreover, maternal behavior did not seem to mediate the transgenerational effect we found, although repetitive behavior was affected by reproductive experience. These data support a beneficial transgenerational effect of EE on repetitive behavior development and suggest a novel benefit of reproductive experience.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder; Deer mice; Early experience; Maternal behavior; Reproductive experience.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
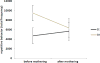
References
-
- Cutuli D, Caporali P, Gelfo F, Angelucci F, Laricchiuta D, Foti F, Bartolo PDe, Bisicchia E, Molinari M, Vecchioli SFarioli, Petrosini L. Pre-reproductive maternal enrichment influences rat maternal care and offspring developmental trajectories: behavioral performances and neuroplasticity correlates, Front. Behav Neurosci. 2015;9:66. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Denenberg VH, Rosenberg KM. Nongenetic transmission of information. Nature. 1967;216:549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

