Impact of Rotavirus Vaccine Introduction and Vaccine Effectiveness in the Republic of Moldova
- PMID: 27059348
- PMCID: PMC7958309
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ1209
Impact of Rotavirus Vaccine Introduction and Vaccine Effectiveness in the Republic of Moldova
Abstract
Background: The Republic of Moldova was the first low- to middle-income country in the World Health Organization European Region to introduce rotavirus vaccine (July 2012). We aimed to assess the impact of the rotavirus vaccine program and estimate vaccine effectiveness (VE).
Methods: Surveillance for rotavirus gastroenteritis was conducted in 2 hospitals in the capital city of Chisinau starting in September 2009. Monthly rotavirus admissions by age were examined before and after introduction of rotavirus vaccination using interrupted time-series analyses. We performed a case-control study of VE by comparing rotavirus case patients with test-negative controls.
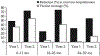
Results: Coverage with at least 1 dose of vaccine increased from 35% in year 1 to 55% in year 2 for children <1 year of age. The percentage of hospital admissions positive for rotavirus fell from 45% in the prevaccine period to 25% (rate reduction, 36%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 26%-44%) and 14% (rate reduction, 67%; 95% CI, 48%-88%) in the first and second years after vaccine introduction, respectively, among children aged <5 years. Reductions were most pronounced among those aged <1 year. Significant reductions among cohorts too old to be vaccinated suggest indirect benefits. Two-dose VE was 79% (95% CI, 62%-88%) against rotavirus hospitalization and 84% (95% CI, 64%-93%) against moderate to severe rotavirus.
Conclusions: These results consistently point to profound direct and herd immunity impacts of the rotavirus vaccine program in young children in the Republic of Moldova. Vaccine coverage was modest in these early years following introduction, so there remains potential for further disease reductions.
Keywords: Moldova; case-control; rotavirus; surveillance; vaccine effectiveness.
Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2016. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, et al. 2008 estimate of worldwide rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination programmes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2012; 12:136–41. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet 2012; 379:2151–61. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015; 385:430–40. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Generic protocols for (i) hospital-based surveillance to estimate the burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children and (ii) a community-based survey on utilization of health care services for gastroenteritis in children. Geneva, Switzerland. 2002. Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/67743/1/WHO_V-B_02.15_eng.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

