Adipokines and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Normal Human Breast Tissue in Vivo - Correlations and Attenuation by Dietary Flaxseed
- PMID: 27059487
- PMCID: PMC4933741
- DOI: 10.1007/s10911-016-9352-9
Adipokines and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Normal Human Breast Tissue in Vivo - Correlations and Attenuation by Dietary Flaxseed
Abstract
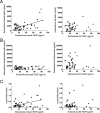
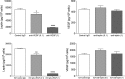
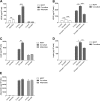
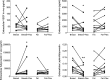
Exposure to sex steroids increases the risk of breast cancer but the exact mechanisms are yet to be elucidated. Events in the microenvironment are important for carcinogenesis. Diet containing phytoestrogens can affect the breast microenvironment and alter the risk of breast cancer. It has previously been shown that estrogen regulates extracellular levels of leptin, adiponectin, and VEGF in normal breast tissue in vivo. Whether these proteins correlate in breast tissue in vivo or if diet addition of flaxseed, a major source of phytoestrogens in Western diets, alters adipokine levels in breast tissue are unknown. We used microdialysis to sample proteins of normal human breast tissue and abdominal subcutaneous fat in situ in 34 pre-and postmenopausal women. In vitro, co-culture of breast cancer cells and primary human adipocytes was used. In vivo, in normal breast tissue, a significant positive correlation between VEGF and leptin was detected. No correlations were found in fat tissue. Co-culture of adipocytes and breast cancer cells per se increased the secretion of VEGF and leptin and enhanced the effects of estradiol compared to culture of either cell type alone. In vitro, inhibition of VEGF diminished the release of leptin while inhibition of leptin had no influence on VEGF secretion. The levels of leptin decreased and adiponectin increased after a dietary addition of 25 g of flaxseed/day for one menstrual cycle. We conclude that VEGF and leptin correlate significantly in normal human breast tissue in vivo and that dietary addition of flaxseed affect adipokine levels in the breast.
Keywords: Adiponectin; Diet; Estrogen; Flaxseed; Leptin; Microdialysis.
Figures
References
-
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, Dowsett M, Knox J, Cawthorn S, et al. Anastrozole for prevention of breast cancer in high-risk postmenopausal women (IBIS-II): an international, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383(9922):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62292-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

