Apoptotic Debris Accumulates on Hematopoietic Cells and Promotes Disease in Murine and Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 27059595
- PMCID: PMC4868781
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500418
Apoptotic Debris Accumulates on Hematopoietic Cells and Promotes Disease in Murine and Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
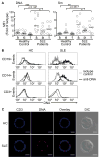
Apoptotic debris, autoantibody, and IgG-immune complexes (ICs) have long been implicated in the inflammation associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); however, it remains unclear whether they initiate immune-mediated events that promote disease. In this study, we show that PBMCs from SLE patients experiencing active disease, and hematopoietic cells from lupus-prone MRL/lpr and NZM2410 mice accumulate markedly elevated levels of surface-bound nuclear self-antigens. On dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages (MFs), the self-antigens are part of IgG-ICs that promote FcγRI-mediated signal transduction. Accumulation of IgG-ICs is evident on ex vivo myeloid cells from MRL/lpr mice by 10 wk of age and steadily increases prior to lupus nephritis. IgG and FcγRI play a critical role in disease pathology. Passive transfer of pathogenic IgG into IgG-deficient MRL/lpr mice promotes the accumulation of IgG-ICs prior to significant B cell expansion, BAFF secretion, and lupus nephritis. In contrast, diminishing the burden IgG-ICs in MRL/lpr mice through deficiency in FcγRI markedly improves these lupus pathologies. Taken together, our findings reveal a previously unappreciated role for the cell surface accumulation of IgG-ICs in human and murine lupus.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A benzenediamine derivate FC-99 attenuates lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice via inhibiting myeloid dendritic cell-secreted BAFF.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016 May;48(5):411-9. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmw017. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016. PMID: 27121231 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) deficiency delays lupus nephritis in MRL-Faslpr mice: the IL-6 pathway as a new therapeutic target in treatment of autoimmune kidney disease in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Rheumatol. 2010 Jan;37(1):60-70. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.090194. Epub 2009 Dec 1. J Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 19955044
-
AID dysregulation in lupus-prone MRL/Fas(lpr/lpr) mice increases class switch DNA recombination and promotes interchromosomal c-Myc/IgH loci translocations: modulation by HoxC4.Autoimmunity. 2011 Dec;44(8):585-98. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2011.577128. Epub 2011 May 18. Autoimmunity. 2011. PMID: 21585311 Free PMC article.
-
Use of genetic knockouts to modulate disease expression in a murine model of lupus, MRL/lpr mice.Immunol Res. 2002;25(2):143-53. doi: 10.1385/ir:25:2:143. Immunol Res. 2002. PMID: 11999168 Review.
-
The central and multiple roles of B cells in lupus pathogenesis.Immunol Rev. 1999 Jun;169:107-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01310.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10450512 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating Pentraxin3-Specific B Cells Are Decreased in Lupus Nephritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 25;10:29. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00029. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30740098 Free PMC article.
-
BAFF Induces Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Positions T Cells within the Glomeruli during Lupus Nephritis.J Immunol. 2017 Apr 1;198(7):2602-2611. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600281. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28235864 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 regulate the proliferation and differentiation of B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 15;14:1093208. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1093208. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omega-3 Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Impedes Silica-Induced Macrophage Corpse Accumulation by Attenuating Cell Death and Potentiating Efferocytosis.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 6;11:2179. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02179. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33123123 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis in lupus mice identifies Coronin-1A as a potential biomarker for lupus nephritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Jun 18;22(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02236-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32552896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deapen D, Escalante A, Weinrib L, Horwitz D, Bachman B, Roy-Burman P, Walker A, Mack TM. A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM. Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006;28:119–130. - PubMed
-
- Bardana EJ, Jr, Harbeck RJ, Hoffman AA, Pirofsky B, Carr RI. The prognostic and therapeutic implications of DNA:anti-DNA immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Am J Med. 1975;59:515–522. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S, Hanayama R, Kawane K. Autoimmunity and the clearance of dead cells. Cell. 2010;140:619–630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

