CollapsABEL: an R library for detecting compound heterozygote alleles in genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 27059780
- PMCID: PMC4826552
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1006-9
CollapsABEL: an R library for detecting compound heterozygote alleles in genome-wide association studies
Abstract
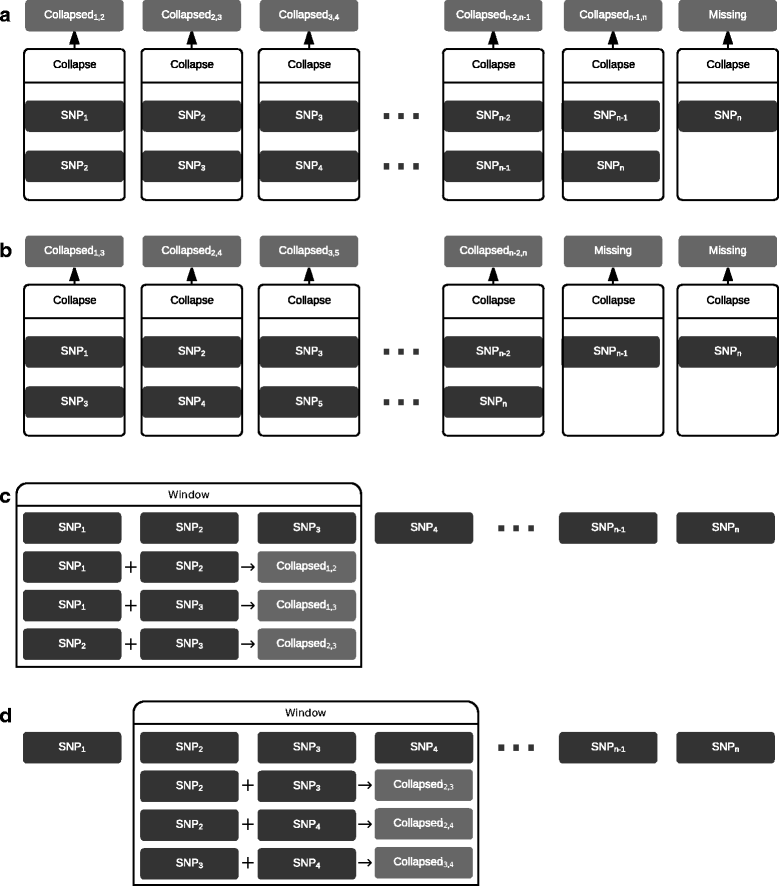
Background: Compound Heterozygosity (CH) in classical genetics is the presence of two different recessive mutations at a particular gene locus. A relaxed form of CH alleles may account for an essential proportion of the missing heritability, i.e. heritability of phenotypes so far not accounted for by single genetic variants. Methods to detect CH-like effects in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) may facilitate explaining the missing heritability, but to our knowledge no viable software tools for this purpose are currently available.
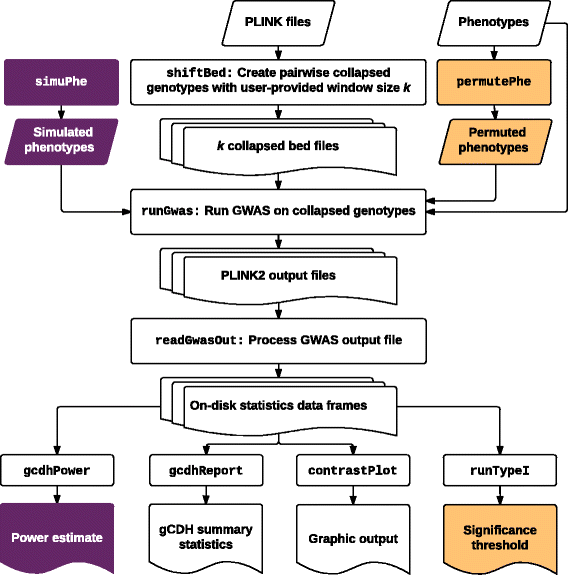
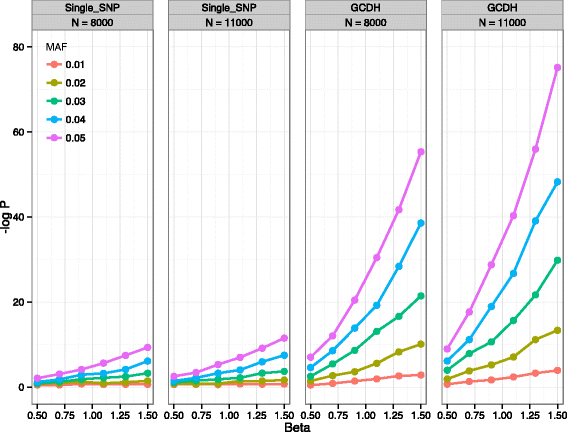
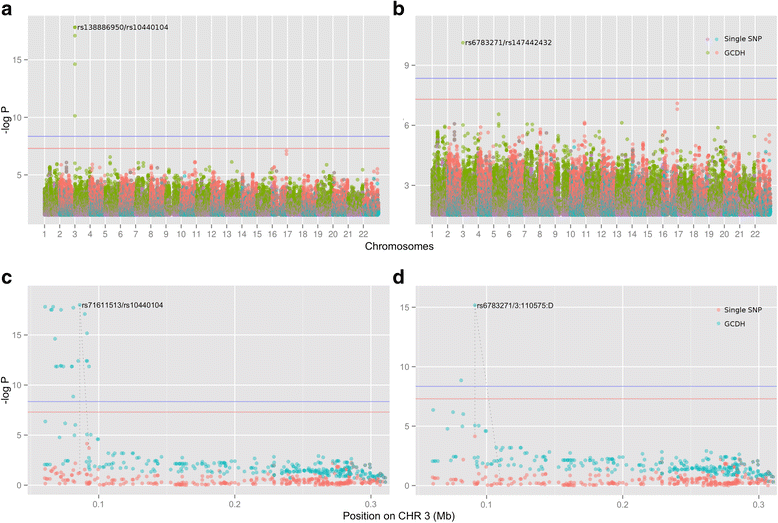
Results: In this work we present the Generalized Compound Double Heterozygosity (GCDH) test and its implementation in the R package CollapsABEL. Time-consuming procedures are optimized for computational efficiency using Java or C++. Intermediate results are stored either in an SQL database or in a so-called big.matrix file to achieve reasonable memory footprint. Our large scale simulation studies show that GCDH is capable of discovering genetic associations due to CH-like interactions with much higher power than a conventional single-SNP approach under various settings, whether the causal genetic variations are available or not. CollapsABEL provides a user-friendly pipeline for genotype collapsing, statistical testing, power estimation, type I error control and graphics generation in the R language.
Conclusions: CollapsABEL provides a computationally efficient solution for screening general forms of CH alleles in densely imputed microarray or whole genome sequencing datasets. The GCDH test provides an improved power over single-SNP based methods in detecting the prevalence of CH in human complex phenotypes, offering an opportunity for tackling the missing heritability problem. Binary and source packages of CollapsABEL are available on CRAN ( https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/CollapsABEL ) and the website of the GenABEL project ( http://www.genabel.org/packages ).
Keywords: Compound heterozygosity; Genome wide association study; Missing heritability; Next generation sequencing.
Figures
References
-
- Schaaf CP, Zschocke J, Potocki L: Human Genetics: from molecules to medicine. Philadelphia, USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

