Lipoxin A4 inhibits microglial activation and reduces neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain after spinal cord hemisection
- PMID: 27059991
- PMCID: PMC4826542
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0540-8
Lipoxin A4 inhibits microglial activation and reduces neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain after spinal cord hemisection
Abstract
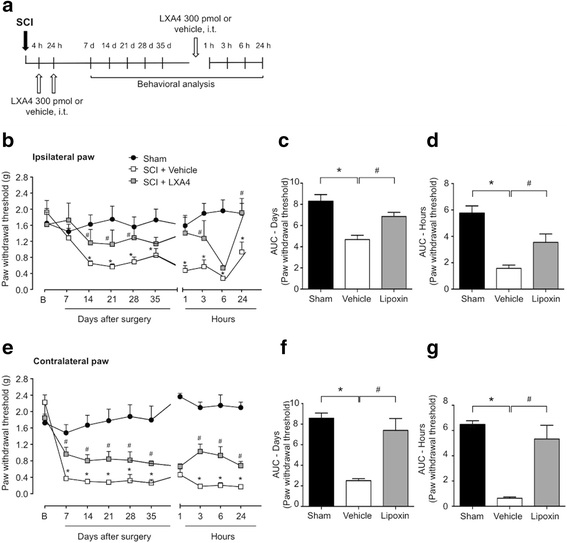
Background: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a severe neurological disorder with many disabling consequences, including persistent neuropathic pain, which develops in about 40 % of SCI patients and is induced and sustained by excessive and uncontrolled spinal neuroinflammation. Here, we have evaluated the effects of lipoxin A4 (LXA4), a member of a unique class of endogenous lipid mediators with both anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, on spinal neuroinflammation and chronic pain in an experimental model of SCI.
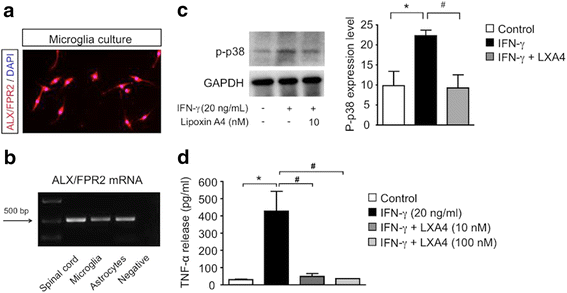
Methods: Spinal hemisection at T10 was carried out in adult male CD1 mice and Wistar rats. To test if LXA4 can reduce neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain, each animal received two intrathecal injections of LXA4 (300 pmol) or vehicle at 4 and 24 h after SCI. Sensitivity to mechanical stimulation of the hind paws was evaluated using von Frey monofilaments, and neuroinflammation was tested by measuring the mRNA and/or protein expression levels of glial markers and cytokines in the spinal cord samples after SCI. Also, microglia cultures prepared from murine cortical tissue were used to assess the direct effects of LXA4 on microglial activation and release of pro-inflammatory TNF-α.
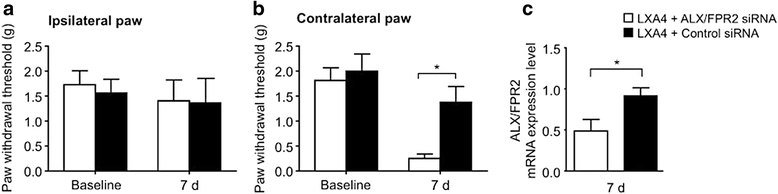
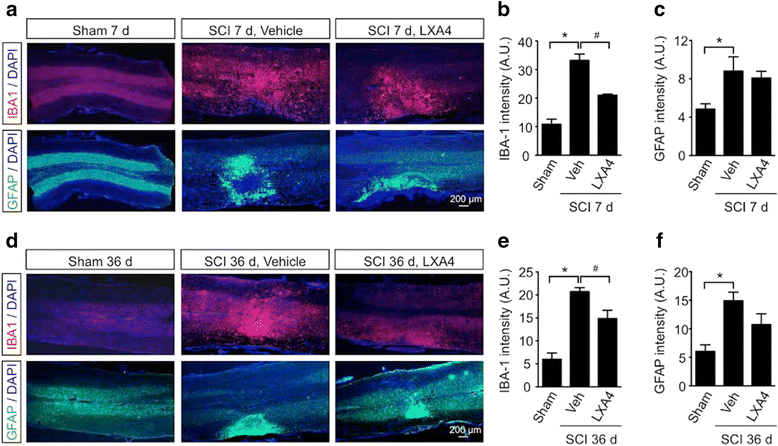
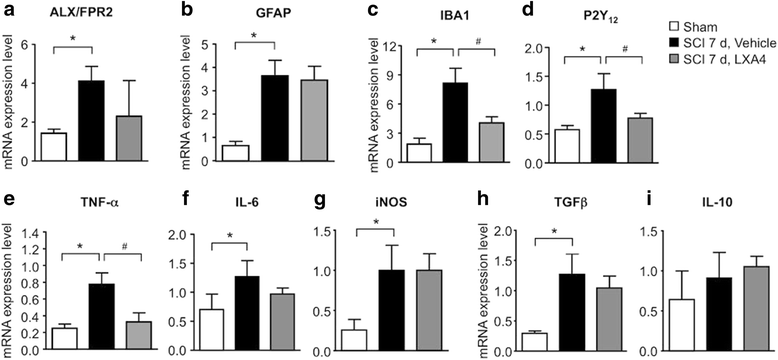
Results: LXA4 treatment caused significant reductions in the intensity of mechanical pain hypersensitivity and spinal expression levels of microglial markers and pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by SCI, when compared to rodents receiving control vehicle injections. Notably, the increased expressions of the microglial marker IBA-1 and of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α were the most affected by the LXA4 treatment. Furthermore, cortical microglial cultures expressed ALX/FPR2 receptors for LXA4 and displayed potentially anti-inflammatory responses upon challenge with LXA4.
Conclusions: Collectively, our results suggest that LXA4 can effectively modulate microglial activation and TNF-α release through ALX/FPR2 receptors, ultimately reducing neuropathic pain in rodents after spinal cord hemisection. The dual anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of LXA4, allied to its endogenous nature and safety profile, may render this lipid mediator as new therapeutic approach for treating various neuroinflammatory disorders and chronic pain with only limited side effects.
Keywords: Chronic pain; Lipoxin; Microglia; Neuroinflammation; Spinal cord injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspirin-triggered Lipoxin A4 attenuates mechanical allodynia in association with inhibiting spinal JAK2/STAT3 signaling in neuropathic pain in rats.Neuroscience. 2014 Jul 25;273:65-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.04.052. Epub 2014 May 14. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24836854
-
Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered lipoxin alleviate bone cancer pain in association with suppressing expression of spinal proinflammatory cytokines.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Dec 26;9:278. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-278. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 23268791 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxin A4 attenuates radicular pain possibly by inhibiting spinal ERK, JNK and NF-κB/p65 and cytokine signals, but not p38, in a rat model of non-compressive lumbar disc herniation.Neuroscience. 2015 Aug 6;300:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.04.060. Epub 2015 May 2. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25943485
-
Systematic analysis of critical genes and pathways identified a signature of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury.Eur J Neurosci. 2022 Jul;56(2):3991-4008. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15693. Epub 2022 May 27. Eur J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35560852 Review.
-
Mechanisms and Therapeutic Prospects of Microglia-Astrocyte Interactions in Neuropathic Pain Following Spinal Cord Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;62(4):4654-4676. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04562-1. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39470872 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Lipoxin A4 and B4 Signaling on the Inner Retina in a Mouse Model of Experimental Glaucoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 19:2024.01.17.575414. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.17.575414. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38293224 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
MC4R Is Involved in Neuropathic Pain by Regulating JNK Signaling Pathway After Chronic Constriction Injury.Front Neurosci. 2019 Sep 10;13:919. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00919. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31551683 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting Edge: Human Vagus Produces Specialized Proresolving Mediators of Inflammation with Electrical Stimulation Reducing Proinflammatory Eicosanoids.J Immunol. 2018 Dec 1;201(11):3161-3165. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800806. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30355784 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-mediated elevation of the specialized pro-resolving lipid mediator levels in a Sjögren's syndrome mouse model.FASEB J. 2020 Jun;34(6):7733-7744. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902196R. Epub 2020 Apr 11. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32277856 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal-Glial Interactions Maintain Chronic Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:2480689. doi: 10.1155/2017/2480689. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 28951789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bickenbach et al. ISCoS-WHO collaboration. International Perspecties of Spinal Cord Injury (IPSCI). 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

