Integrated regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor phosphorylation in the striatum by dopamine and acetylcholine
- PMID: 27060412
- PMCID: PMC5055431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.04.005
Integrated regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor phosphorylation in the striatum by dopamine and acetylcholine
Abstract
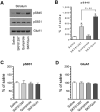
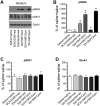
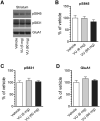
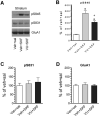
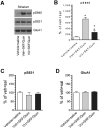
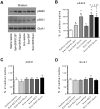
Dopamine (DA) and acetylcholine (ACh) signals converge onto protein kinase A (PKA) in medium spiny neurons of the striatum to control cellular and synaptic activities of these neurons, although underlying molecular mechanisms are less clear. Here we measured phosphorylation of the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor (AMPAR) at a PKA site (S845) as an indicator of AMPAR responses in adult rat brains in vivo to explore how DA and ACh interact to modulate AMPARs. We found that subtype-selective activation of DA D1 receptors (D1Rs), D2 receptors (D2Rs), or muscarinic M4 receptors (M4Rs) induced specific patterns of GluA1 S845 responses in the striatum. These defined patterns support a local multitransmitter interaction model in which D2Rs inhibited an intrinsic inhibitory element mediated by M4Rs to enhance the D1R efficacy in modulating AMPARs. Consistent with this, selective enhancement of M4R activity by a positive allosteric modulator resumed the cholinergic inhibition of D1Rs. In addition, D1R and D2R coactivation recruited GluA1 and PKA preferentially to extrasynaptic sites. In sum, our in vivo data support an existence of a dynamic DA-ACh balance in the striatum which actively modulates GluA1 AMPAR phosphorylation and trafficking. This article is part of the Special Issue entitled 'Ionotropic glutamate receptors'.
Keywords: (-)-quinpirole hydrochloride (PubChem CID:55397); (-)-scopolamine hydrobromide (PubChem CID:517999); Caudate putamen; D1; D2; Muscarinic receptor; Nucleus accumbens; Positive allosteric modulator; Protein kinase A; S-(-)-eticlopride hydrochloride (PubChem CID:11973707); S845; SCH23390 (PubChem CID:5018); SKF81297 (PubChem CID:1218); VU0152100 (PubChem CID:864492).
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Acquas E, Di Chiara G. Role of dopamine D1 receptors in the control of striatal acetylcholine release by endogenous dopamine. Neurol Sci. 2001;22:41–42. - PubMed
-
- Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB. The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1989;12:366–375. - PubMed
-
- Aubert I, Ghorayeb I, Normand E, Bloch B. Phenotypical characterization of the neurons expressing the D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the monkey striatum. J Comp Neurol. 2000;418:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Derkach V, Soderling T. Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate-type glutamate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32727–32730. - PubMed
-
- Bernard V, Dumartin B, Lamy E, Bloch B. Fos immunoreactivity after stimulation or inhibition of muscarinic receptors indicates anatomical specificity for cholinergic control of striatal efferent neurons and cortical neurons in the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 1993;5:1218–1225. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

