An investigation into the role of ATP in the mammalian pre-mRNA 3' cleavage reaction
- PMID: 27060432
- PMCID: PMC5039938
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.04.004
An investigation into the role of ATP in the mammalian pre-mRNA 3' cleavage reaction
Abstract
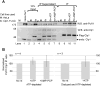
RNA Polymerase II transcribes beyond what later becomes the 3' end of a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). The formation of most mRNA 3' ends results from pre-mRNA cleavage followed by polyadenylation. In vitro studies have shown that low concentrations of ATP stimulate the 3' cleavage reaction while high concentrations inhibit it, but the origin of these ATP effects is unknown. ATP might enable a cleavage factor kinase or activate a cleavage factor directly. To distinguish between these possibilities, we tested several ATP structural analogs in a pre-mRNA 3' cleavage reaction reconstituted from DEAE-fractionated cleavage factors. We found that adenosine 5'-(β,γ-methylene)triphosphate (AMP-PCP) is an effective in vitro 3' cleavage inhibitor with an IC50 of ∼300 μM, but that most other ATP analogs, including adenosine 5'-(β,γ-imido)triphosphate, which cannot serve as a protein kinase substrate, promoted 3' cleavage but less efficiently than ATP. In combination with previous literature data, our results do not support ATP stimulation of 3' cleavage through cleavage factor phosphorylation in vitro. Instead, the more likely mechanism is that ATP stimulates cleavage factor activity through direct cleavage factor binding. The mammalian 3' cleavage factors known to bind ATP include the cleavage factor II (CF IIm) Clp1 subunit, the CF Im25 subunit and poly(A) polymerase alpha (PAP). The yeast homolog of the CF IIm complex also binds ATP through yClp1. To investigate the mammalian complex, we used a cell-line expressing FLAG-tagged Clp1 to co-immunoprecipitate Pcf11 as a function of ATP concentration. FLAG-Clp1 co-precipitated Pcf11 with or without ATP and the complex was not affected by AMP-PCP. Diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A), an ATP analog that binds the Nudix domain of the CF Im25 subunit with higher affinity than ATP, neither stimulated 3' cleavage in place of ATP nor antagonized ATP-stimulated 3' cleavage. The ATP-binding site of PAP was disrupted by site directed mutagenesis but a reconstituted 3' cleavage reaction containing a mutant PAP unable to bind ATP nevertheless underwent ATP-stimulated 3' cleavage. Fluctuating ATP levels might contribute to the regulation of pre-mRNA 3' cleavage, but the three subunits investigated here do not appear to be responsible for the ATP-stimulation of pre-mRNA cleavage.
Keywords: 3′ End formation; ATP; Cleavage and polyadenylation; Pre-mRNA processing.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. and Société Française de Biochimie et Biologie Moléculaire (SFBBM). All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



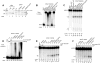
Similar articles
-
The P-loop domain of yeast Clp1 mediates interactions between CF IA and CPF factors in pre-mRNA 3' end formation.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029139. Epub 2011 Dec 22. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22216186 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of Pcf11 and Clp1 is needed for mRNA 3'-end formation and is modulated by amino acids in the ATP-binding site.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(3):1214-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr801. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21993299 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage factor II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains homologues to subunits of the mammalian Cleavage/ polyadenylation specificity factor and exhibits sequence-specific, ATP-dependent interaction with precursor RNA.J Biol Chem. 1997 Apr 18;272(16):10831-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.16.10831. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9099738
-
Architectural and functional details of CF IA proteins involved in yeast 3'-end pre-mRNA processing and its significance for eukaryotes: A concise review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 15;193(Pt A):387-400. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.129. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34699898 Review.
-
What nuclease cleaves pre-mRNA in the process of polyadenylation?IUBMB Life. 2002 Jul;54(1):27-31. doi: 10.1080/15216540213821. IUBMB Life. 2002. PMID: 12387572 Review.
Cited by
-
Re-evaluation of Diadenosine Tetraphosphate (Ap4A) From a Stress Metabolite to Bona Fide Secondary Messenger.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 17;7:606807. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.606807. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33282915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(A) tail dynamics: Measuring polyadenylation, deadenylation and poly(A) tail length.Methods Enzymol. 2021;655:265-290. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2021.04.005. Epub 2021 May 3. Methods Enzymol. 2021. PMID: 34183126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beyer K, Dandekar T, Keller W. RNA ligands selected by cleavage stimulation factor contain distinct sequence motifs that function as downstream elements in 3′-end processing of pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:26769–26779. - PubMed
-
- Bienroth S, Wahle E, Suter-Crazzolara C, Keller W. Purification of the cleavage and polyadenylation factor involved in the 3′-processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:19768–19776. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

