Probing the activity of a non-oxime reactivator for acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents
- PMID: 27062893
- PMCID: PMC11525883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.04.002
Probing the activity of a non-oxime reactivator for acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents
Abstract
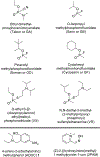
Currently fielded treatments for nerve agent intoxication include atropine, an acetylcholine receptor antagonist, and pralidoxime (2PAM), a small molecule reactivator of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). 2PAM reactivates nerve agent-inhibited AChE via direct nucleophilic attack by the oxime moiety on the phosphorus center of the bound nerve agent. Due to a permanently charged pyridinium motif, 2PAM is not thought to cross the blood brain barrier and therefore cannot act directly in the neuronal junctions of the brain. In this study, ADOC, a non-permanently charged, non-oxime molecule initially identified using pesticide-inhibited AChE, was characterized in vitro against nerve agent-inhibited recombinant human AChE. The inhibitory and reactivation potentials of ADOC were determined with native AChE and AChE inhibited with tabun, sarin, soman, cyclosarin, VX, or VR and then compared to those of 2PAM. Several structural analogs of ADOC were used to probe the reactivation mechanism of the molecule. Finally, guinea pigs were used to examine the protective efficacy of the compound after exposure to sarin. The results of both in vitro and in vivo testing will be useful in the design of future small molecule reactivators.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Guinea pig; Organophosphorus nerve agent; Oxime; Pralidoxime; Reactivator.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
None.
Figures
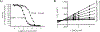
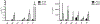
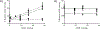
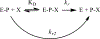
References
-
- Dunn MA and Sidell FR, Progress in medical defense against nerve agents. JAMA, 1989. 262(5): p. 649–52. - PubMed
-
- Millard CB, et al., Crystal structures of aged phosphonylated acetylcholinesterase: nerve agent reaction products at the atomic level. Biochemistry, 1999. 38(22): p. 7032–9. - PubMed
-
- Skovira JW, et al., Reactivation of brain acetylcholinesterase by monoisonitrosoacetone increases the therapeutic efficacy against nerve agents in guinea pigs. Chem Biol Interact, 2010. 187(1–3): p. 318–24. - PubMed
-
- Rosman Y, et al., Lessons learned from the Syrian sarin attack: evaluation of a clinical syndrome through social media. Ann Intern Med, 2014. 160(9): p. 644–8. - PubMed
-
- Smithson A. and Levy L, Ataxia: The Chemical and Biological Terrorism Threat and the US Response. 2000, Washington, DC: Henry L Stimson Centre.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

