Splicing misregulation of SCN5A contributes to cardiac-conduction delay and heart arrhythmia in myotonic dystrophy
- PMID: 27063795
- PMCID: PMC4831019
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11067
Splicing misregulation of SCN5A contributes to cardiac-conduction delay and heart arrhythmia in myotonic dystrophy
Abstract
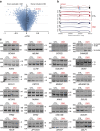
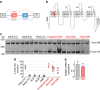
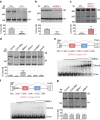
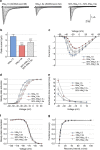
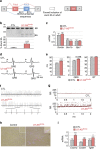
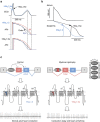
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is caused by the expression of mutant RNAs containing expanded CUG repeats that sequester muscleblind-like (MBNL) proteins, leading to alternative splicing changes. Cardiac alterations, characterized by conduction delays and arrhythmia, are the second most common cause of death in DM. Using RNA sequencing, here we identify novel splicing alterations in DM heart samples, including a switch from adult exon 6B towards fetal exon 6A in the cardiac sodium channel, SCN5A. We find that MBNL1 regulates alternative splicing of SCN5A mRNA and that the splicing variant of SCN5A produced in DM presents a reduced excitability compared with the control adult isoform. Importantly, reproducing splicing alteration of Scn5a in mice is sufficient to promote heart arrhythmia and cardiac-conduction delay, two predominant features of myotonic dystrophy. In conclusion, misregulation of the alternative splicing of SCN5A may contribute to a subset of the cardiac dysfunctions observed in myotonic dystrophy.
Figures

References
-
- Brook J. D. et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 68, 799–808 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Fu Y. H. et al. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 255, 1256–1258 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Mahadevan M. et al. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science 255, 1253–1255 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Liquori C. L. et al. Myotonic dystrophy type 2 caused by a CCTG expansion in intron 1 of ZNF9. Science 293, 864–867 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

