Dynamic Characteristics of Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Chinese Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving 7 Years of Entecavir Therapy
- PMID: 27064037
- PMCID: PMC4831527
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.179802
Dynamic Characteristics of Serum Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Chinese Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving 7 Years of Entecavir Therapy
Abstract
Background: The ultimate goal of hepatitis B treatment is hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance. Several factors have been suggested to be associated with the rate of HBsAg reduction in antiviral-naive or lamivudine therapy cohorts. However, there are few studies evaluating the factors during long-term entecavir (ETV) therapy. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the factors to predict the outcome of ETV therapy for 7 years.
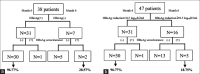
Methods: A total of 47 chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients treated with ETV monotherapy were included in this study. Liver biochemistry, hepatitis B virus (HBV) serological markers, serum HBV DNA, and HBsAg titers were tested at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and yearly from 1 to 7. The associations between factors and HBsAg reduction were assessed using multivariate tests with repeated measure analysis of variance.
Results: At baseline, serum HBsAg levels showed a positive correlation with baseline HBV DNA levels (r = 0.625, P < 0.001). The mean HBsAg titers after ETV treatment were significantly lower than the baseline titers (P ranges from 0.025 to 0.000,000,6). The HBsAg reduction rate during the 1st year was greater compared to after 1 year of treatment (P < 0.05). Multivariate test showed that hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) seroclearance and/or HBsAg reduction ≥0.5 log10 IU/ml at 6 months had a high negative predictive value (96.77%) for HBsAg seroclearance (P = 0.002, P = 0.012, respectively).
Conclusions: The HBsAg reduction rate during the 1st year was greater than that after 1 year of treatment. Further, HBeAg status and HBsAg levels at month 6 are the optimal factors for the early prediction of HBsAg seroclearance after long-term ETV therapy in CHB patients.
Figures



References
-
- Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection –Natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1118–29. doi:10.1056/NEJMra031087. - PubMed
-
- Jiang DK, Wu X, Qian J, Ma XP, Yang J, Li Z, et al. Genetic variation in STAT4 predicts response to interferon-alpha therapy for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2015 [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1002/hep.28423. - PubMed
-
- Wang YJ, Yang L, Zuo JP. Recent developments in antivirals against hepatitis B virus. Virus Res. 2015;213:205–13. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2015.12.014. - PubMed
-
- Wong DK, Seto WK, Fung J, Ip P, Huang FY, Lai CL, et al. Reduction of hepatitis B surface antigen and covalently closed circular DNA by nucleos(t)ide analogues of different potency. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1004–10.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2013.01.026. - PubMed
-
- Li GJ, Yu YQ, Chen SL, Fan P, Shao LY, Chen JZ, et al. Sequential combination therapy with pegylated interferon leads to loss of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving long-term entecavir treatment. Antimicrob Agents chemother. 2015;59:4121–8. doi:10.1128/AAC.00249-15. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

