Different Risk of Tuberculosis and Efficacy of Isoniazid Prophylaxis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Biologic Therapy: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study in Taiwan
- PMID: 27064275
- PMCID: PMC4827833
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153217
Different Risk of Tuberculosis and Efficacy of Isoniazid Prophylaxis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Biologic Therapy: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study in Taiwan
Abstract
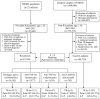
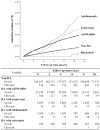
Increasing evidence indicates an increased risk of tuberculosis (TB) for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients receiving biologic therapy, and the effectiveness of isoniazid prophylaxis (INHP) in TB prevention. We aimed to examine 1) the incidence rate (IR) and risk factors for TB among RA patients receiving different therapies; 2) INHP effectiveness for TB prevention; 3) mortality rates after TB diagnosis in patients receiving different therapies. This retrospective study was conducted using a nationwide database: 168,720 non-RA subjects and a total of 42,180 RA patients including 36,162 csDMARDs-exposed, 3,577 etanercept-exposed, 1,678 adalimumab-exposed and 763 rituximab-exposed patients. TB risk was 2.7-fold higher in RA cohort compared with non-RA group, with an adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) of 2.58. Advanced age, male, the use of corticosteroids ≧ 5 mg/day, and the presence of diabetes mellitus (DM), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic kidney disease were risk factors for developing TB. Using csDMARDs-exposed group as reference, aHR of TB was the highest with adalimumab treatment (1.52), followed by etanercept (1.16), and the lowest with rituximab (0.08). INHP could effectively reduce TB risk in biologics-exposed patients. Mortality rates after TB diagnosis were higher in RA patients, particularly the elderly and those with DM, with lower rates in adalimumab-exposed patients compared with csDMARDs-exposed patients. In conclusion, TB risk was increased in patients receiving TNF-α inhibitors, but the risk associated with rituximab therapy was relatively low. With the effectiveness of INHP shown in the prevention of biologics-associated TB, stricter implementation of INHP should be beneficial. The mortality from biologics-associated TB may be efficiently reduced through increased awareness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
One-Year Tuberculosis Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Starting Their First Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy from 2008 to 2012 in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 10;11(11):e0166339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166339. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27832150 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of active tuberculosis in patients with inflammatory arthritis receiving TNF inhibitors: a look beyond the baseline tuberculosis screening protocol.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Sep;37(9):2391-2397. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3916-y. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29150737
-
Risk of tuberculosis, serious infection and lymphoma with disease-modifying biologic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Taiwan.Int J Rheum Dis. 2014 Dec;17 Suppl 3:9-19. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12539. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 25496045
-
The Risk of Tuberculosis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Antagonist: A Metaanalysis of Both Randomized Controlled Trials and Registry/Cohort Studies.J Rheumatol. 2015 Dec;42(12):2229-37. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150057. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26472414 Review.
-
Infection risk in patients undergoing treatment for inflammatory arthritis: non-biologics versus biologics.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020 Feb;16(2):207-228. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1705785. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31852268 Review.
Cited by
-
Peritoneal tuberculosis in the setting of ustekinumab treatment for psoriasis.JAAD Case Rep. 2017 Apr 14;3(3):230-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.02.001. eCollection 2017 May. JAAD Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28443318 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Incident tuberculosis disease in patients receiving biologic therapies in the Western Cape, South Africa from 2007 to 2018.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Nov 30;20(1):900. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05624-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33256634 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Trends in Total Knee and Hip Arthroplasties for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis vs. the General Population-A 14-Year Retrospective Study in Taiwan.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 20;8:640275. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.640275. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33959623 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis and targeted synthetic or biologic DMARDs, beyond tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2020 Jun 22;12:1759720X20930116. doi: 10.1177/1759720X20930116. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2020. PMID: 32612710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of cancer development on the risk of mycobacterial diseases among rheumatoid arthritis patients.Epidemiol Infect. 2017 Sep;145(12):2482-2490. doi: 10.1017/S0950268817001534. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Epidemiol Infect. 2017. PMID: 28737121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2014. Available: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. 2014.
-
- Centers for Disease Control, R.O.C. (Taiwan). Taiwan Tuberculosis Control Report 2013. 2013.
-
- Doran MF, Crowson CS, Pond GR, O'Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. Frequency of infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:2287–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

