High-Resolution Ultrasonography of the Superficial Peroneal Motor and Sural Sensory Nerves May Be a Non-invasive Approach to the Diagnosis of Vasculitic Neuropathy
- PMID: 27064457
- PMCID: PMC4812111
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00048
High-Resolution Ultrasonography of the Superficial Peroneal Motor and Sural Sensory Nerves May Be a Non-invasive Approach to the Diagnosis of Vasculitic Neuropathy
Abstract
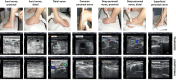
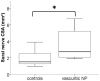
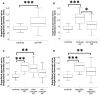
High-resolution ultrasonography (HRUS) is an emerging new tool in the investigation of peripheral nerves. We set out to assess the utility of HRUS performed at lower extremity nerves in peripheral neuropathies. Nerves of 26 patients with polyneuropathies of different etiologies and 26 controls were investigated using HRUS. Patients underwent clinical, laboratory, electrophysiological assessment, and a diagnostic sural nerve biopsy as part of the routine work-up. HRUS was performed at the sural, tibial, and the common, superficial, and deep peroneal nerves. The superficial peroneal nerve longitudinal diameter (LD) distinguished best between the groups: patients with immune-mediated neuropathies (n = 13, including six with histology-proven vasculitic neuropathy) had larger LD compared to patients with non-immune-mediated neuropathies (p < 0.05) and to controls (p < 0.001). Among all subgroups, patients with vasculitic neuropathy showed the largest superficial peroneal nerve LD (p < 0.001) and had a larger sural nerve cross-sectional area when compared with disease controls (p < 0.001). Enlargement of the superficial peroneal and sural nerves as detected by HRUS may be a useful additional finding in the differential diagnosis of vasculitic and other immune-mediated neuropathies.
Keywords: nerve ultrasonography; peripheral neuropathy; superficial peroneal nerve; sural nerve; vasculitis.
Figures
References
-
- Collins MP, Dyck PJ, Gronseth GS, Guillevin L, Hadden RD, Heuss D, et al. Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the classification, diagnosis, investigation, and immunosuppressive therapy of non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy: executive summary. J Peripher Nerv Syst (2010) 15:176–84.10.1111/j.1529-8027.2010.00281.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

