Once vs twice-daily abacavir and lamivudine in African children
- PMID: 27064996
- PMCID: PMC6217915
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001116
Once vs twice-daily abacavir and lamivudine in African children
Abstract
Background: Antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence is critical for successful HIV treatment outcomes. Once-daily dosing could improve adherence. Plasma concentrations of once-daily vs twice-daily abacavir + lamivudine are bioequivalent in children, but no randomized trial has compared virological outcomes.
Methods: Children taking abacavir + lamivudine-containing first-line regimens twice daily for more than 36 weeks in the ARROW trial (NCT02028676, ISRCTN24791884) were randomized to continue twice-daily vs move to once-daily abacavir + lamivudine (open-label). Co-primary outcomes were viral load suppression at week 48 (12% noninferiority margin, measured retrospectively) and lamivudine or abacavir-related grade 3/4 adverse events.
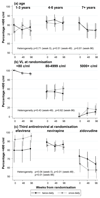
Results: Six hundred and sixty-nine children (median 5 years, range 1-16) were randomized to twice daily (n = 333) vs once daily (n = 336) after median 1.8 years on twice-daily abacavir + lamivudine-containing first-line ART. Children were followed for median 114 weeks. At week 48, 242/331 (73%) twice daily vs 236/330 (72%) once daily had viral load less than 80 copies/ml [difference -1.6% (95% confidence interval -8.4,+5.2%) P = 0.65]; 79% twice daily vs 78% once daily had viral load less than 400 copies/ml (P = 0.76) (week 96 results similar). One grade 3/4 adverse event was judged uncertainly related to abacavir + lamivudine (hepatitis; once daily). At week 48, 9% twice daily vs 10% once daily reported missing one or more ART pills in the last 4 weeks (P = 0.74) and 8 vs 8% at week 96 (P = 0.90). Carers strongly preferred once-daily dosing. There was no difference between randomized groups in postbaseline drug-resistance mutations or drug-susceptibility; WHO 3/4 events; ART-modifying, grade 3/4 or serious adverse events; CD4% or weight-for-age/height-for-age (all P > 0.15).
Conclusion: Once-daily abacavir + lamivudine was noninferior to twice daily in viral load suppression, with similar resistance, adherence, clinical, immunological and safety outcomes. Abacavir + lamivudine provides the first once-daily nucleoside backbone across childhood that can be used to simplify ART.
Conflict of interest statement
WS and NT are employees of ViiV Healthcare (formally GlaxoSmithKline) with associated renumeration (salary stock). ViiV Healthcare/GlaxoSmithKline donated first-line drugs for ARROW and provided funding for VL assays and genotyping. There are no other conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- UNAIDS. 2014 progress report on the Global Plan towards the elimination of new HIV infections among children by 2015 and keeping their mothers alive. 2014.
-
- Nachega JB, Hislop M, Dowdy DW, Chaisson RE, Regensberg L, Maartens G. Adherence to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-based HIV therapy and virologic outcomes. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:564–573. - PubMed
-
- Boyle BA, Jayaweera D, Witt MD, Grimm K, Maa JF, Seekins DW. Randomization to once-daily stavudine extended release/lamivudine/efavirenz versus a more frequent regimen improves adherence while maintaining viral suppression. HIV Clin Trials. 2008;9:164–176. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations fora public health approach. 2013. - PubMed
-
- Lamarca A, Clumeck N, Plettenberg A, Domingo P, Fu K, Craig C, et al. Efficacy and safety of a once-daily fixed-dose combination of abacavir/lamivudine compared with abacavir twice daily and lamivudine once daily as separate entities in antiretroviral-experienced HIV-1-infected patients (CAL30001 Study) J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006;41:598–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

