Deep sequencing and human antibody repertoire analysis
- PMID: 27065089
- PMCID: PMC5203765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.03.008
Deep sequencing and human antibody repertoire analysis
Abstract
In the past decade, high-throughput DNA sequencing (HTS) methods and improved approaches for isolating antigen-specific B cells and their antibody genes have been applied in many areas of human immunology. This work has greatly increased our understanding of human antibody repertoires and the specific clones responsible for protective immunity or immune-mediated pathogenesis. Although the principles underlying selection of individual B cell clones in the intact immune system are still under investigation, the combination of more powerful genetic tracking of antibody lineage development and functional testing of the encoded proteins promises to transform therapeutic antibody discovery and optimization. Here, we highlight recent advances in this fast-moving field.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
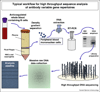
References
-
- Larrick JW, Danielsson L, Brenner CA, Abrahamson M, Fry KE, Borrebaeck CA. Rapid cloning of rearranged immunoglobulin genes from human hybridoma cells using mixed primers and the polymerase chain reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;160:1250–1256. - PubMed
-
- Boyd SD. Diagnostic applications of high-throughput DNA sequencing. Annu Rev Pathol. 2013;8:381–410. - PubMed
-
- Love JC, Ronan JL, Grotenbreg GM, van der Veen AG, Ploegh HL. A microengraving method for rapid selection of single cells producing antigen-specific antibodies. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:703–707. - PubMed
-
-
McDaniel JR, DeKosky BJ, Tanno H, Ellington AD, Georgiou G. Ultra-high-throughput sequencing of the immune receptor repertoire from millions of lymphocytes. Nat Protoc. 2016;11:429–442. This paper gives detailed protocols for building hardware and performing experiments that physically link naturally paired heavy and light chain antibody variable gene amplicons for large-scale repertoire studies.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

