Are Specific Early-Life Adversities Associated With Specific Symptoms of Psychosis?: A Patient Study Considering Just World Beliefs as a Mediator
- PMID: 27065105
- PMCID: PMC4972481
- DOI: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000000511
Are Specific Early-Life Adversities Associated With Specific Symptoms of Psychosis?: A Patient Study Considering Just World Beliefs as a Mediator
Abstract
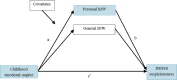
Epidemiological studies have suggested that there may be associations between specific adversities and specific psychotic symptoms. There is also evidence that beliefs about justice may play a role in paranoid symptoms. In this study, we determined whether these associations could be replicated in a patient sample and whether beliefs about a just world played a specific role in the relationship between adversity and paranoia. We examined associations between childhood trauma, belief in justice, and paranoia and hallucinatory experiences in 144 individuals: 72 individuals with a diagnosis of schizophrenia spectrum disorders and 72 comparison controls. There was a dose-response relationship between cumulative trauma and psychosis. When controlling for comorbidity between symptoms, childhood sexual abuse predicted hallucinatory experiences, and experiences of childhood emotional neglect predicted paranoia. The relationship between neglect and paranoia was mediated by a perception of personal injustice. The findings replicate in a patient sample previous observations from epidemiological research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Do specific early-life adversities lead to specific symptoms of psychosis? A study from the 2007 the Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey.Schizophr Bull. 2012 Jun;38(4):734-40. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbs049. Epub 2012 Apr 10. Schizophr Bull. 2012. PMID: 22496540 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences on Psychotic-Like Symptoms and Stress Reactivity in Daily Life in Nonclinical Young Adults.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 15;11(4):e0153557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153557. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27082442 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between specific psychotic symptoms and specific childhood adversities are mediated by attachment styles: an analysis of the National Comorbidity Survey.Psychiatry Res. 2014 Jul 30;217(3):202-9. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.03.019. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Psychiatry Res. 2014. PMID: 24726818
-
Metacognitive beliefs and childhood adversities: an overview of the literature.Psychol Health Med. 2019 Jun;24(5):542-550. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2018.1550258. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Psychol Health Med. 2019. PMID: 30463429 Review.
-
Social Adversity in the Etiology of Psychosis: A Review of the Evidence.Am J Psychother. 2016;70(1):5-33. doi: 10.1176/appi.psychotherapy.2016.70.1.5. Am J Psychother. 2016. PMID: 27052604 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating Specific Associations Between Childhood Victimization Profiles and Positive Psychosis Symptoms: The Mediating Roles of Anxiety, Depression, and Schema.Schizophr Bull Open. 2023 Jun 15;4(1):sgad017. doi: 10.1093/schizbullopen/sgad017. eCollection 2023 Jan. Schizophr Bull Open. 2023. PMID: 37398699 Free PMC article.
-
Interpersonal Violence and Psychotic-Like Experiences: The Mediation of Ideas of Reference, Childhood Memories, and Dissociation.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jun 25;17(12):4587. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17124587. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32630582 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediating Role of Chinese College Students' Control Strategies: Belief in a Just World and Life History Strategy.Front Psychol. 2022 Mar 3;13:844510. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.844510. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35310234 Free PMC article.
-
The role of metacognition and social cognition in childhood trauma effecting on prognosis: 1-year follow-up study in patients with first-episode schizophrenia.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Mar 19;25(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06686-7. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40108572 Free PMC article.
-
Could an evaluative conditioning intervention ameliorate paranoid beliefs? Self-reported and neurophysiological evidence from a brief intervention focused on improving self-esteem.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 23;15:1472332. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1472332. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39507280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajnakina O, Trotta A, Oakley-Hannibal E, di Forti M, Stilo SA, Kolliakou A, Gardner-Sood P, Gaughran F, David AS, Dazzan P, Pariante C, Mondelli V, Morgan C, Vassos E, Murray RM, Fisher HL. (2016) Impact of childhood adversities on specific symptom dimensions in first-episode psychosis. Psychol Med 46:317–26. - PubMed
-
- Alemany S, Goldberg X, van Winkel R, Gastó C, Peralta V, Fañanás L. (2013) Childhood adversity and psychosis: Examining whether the association is due to genetic confounding using a monozygotic twin differences approach. Eur Psychiatry. 28:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Bentall RP. (1990) The illusion of reality: A review and integration of psychological research on hallucinations. Psychol Bull. 107:82–95. - PubMed
-
- Bentall RP, Corcoran R, Howard R, Blackwood N, Kinderman P. (2001) Persecutory delusions: A review and theoretical integration. Clin Psychol Rev. 21:1143–1192. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

