PTH and Vitamin D
- PMID: 27065162
- PMCID: PMC11163478
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c140071
PTH and Vitamin D
Abstract
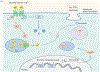
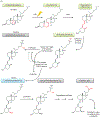
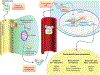
PTH and Vitamin D are two major regulators of mineral metabolism. They play critical roles in the maintenance of calcium and phosphate homeostasis as well as the development and maintenance of bone health. PTH and Vitamin D form a tightly controlled feedback cycle, PTH being a major stimulator of vitamin D synthesis in the kidney while vitamin D exerts negative feedback on PTH secretion. The major function of PTH and major physiologic regulator is circulating ionized calcium. The effects of PTH on gut, kidney, and bone serve to maintain serum calcium within a tight range. PTH has a reciprocal effect on phosphate metabolism. In contrast, vitamin D has a stimulatory effect on both calcium and phosphate homeostasis, playing a key role in providing adequate mineral for normal bone formation. Both hormones act in concert with the more recently discovered FGF23 and klotho, hormones involved predominantly in phosphate metabolism, which also participate in this closely knit feedback circuit. Of great interest are recent studies demonstrating effects of both PTH and vitamin D on the cardiovascular system. Hyperparathyroidism and vitamin D deficiency have been implicated in a variety of cardiovascular disorders including hypertension, atherosclerosis, vascular calcification, and kidney failure. Both hormones have direct effects on the endothelium, heart, and other vascular structures. How these effects of PTH and vitamin D interface with the regulation of bone formation are the subject of intense investigation.
Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Abe Y, Nagasaki K, Watanabe T, Abe T, Fukami M. Association between compound heterozygous mutations of SLC34A3 and hypercalciuria. Horm Res Paediatr 82: 65–71, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Adamczak DM, Nowak JK, Frydrychowicz M, Kaczmarek M, Sikora J. The role of Toll-like receptors and vitamin D in diabetes mellitus type 1–a review. Scand J Immunol 80: 75–84, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Adams AE, Bisello A, Chorev M, Rosenblatt M, Suva LJ. Arginine 186 in the extracellular N-terminal region of the human parathyroid hormone 1 receptor is essential for contact with position 13 of the hormone. Mol Endocrinol (Baltimore, Md) 12: 1673–1683, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Adams JS, Chen H, Chun R, Gacad MA, Encinas C, Ren S, Nguyen L, Wu S, Hewison M, Barsony J. Response element binding proteins and intracellular vitamin D binding proteins: NMovel regulators of vitamin D trafficking, action and metabolism. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 89-90: 461–465, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Adams JS, Clemens TL, Parrish JA, Holick MF. Vitamin-D synthesis and metabolism after ultraviolet irradiation of normal and vitamin-D-deficient subjects. N Engl J Med 306: 722–725, 1982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

