Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Dose-Response Characteristics for Effect of Rhubarb in a Rat Model of Cholestasis
- PMID: 27065293
- PMCID: PMC4814850
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00085
Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Dose-Response Characteristics for Effect of Rhubarb in a Rat Model of Cholestasis
Abstract
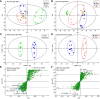
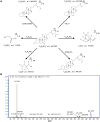
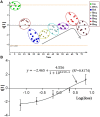
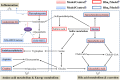
Cholestasis is a serious manifestation of liver diseases with limited therapies. Rhubarb, a widely used herbal medicine, has been frequently used at a relatively large dose for treating cholestasis. However, whether large doses are optimal and the therapeutic mechanism remain unclear. To explore these questions, the anti-cholestatic effect of five doses of rhubarb (0.21, 0.66, 2.10, 6.60, and 21.0 g/kg) in an alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT)-induced rat model of cholestasis was examined by histopathology and serum biochemistry. A dose-dependent anti-cholestatic effect of rhubarb (0.21-6.6 g/kg) was observed, and an overdose of 21.0 g/kg showed a poor effect. LC-MS-based untargeted metabolomics together with pathway analysis were further applied to characterize the metabolic alterations induced by the different rhubarb doses. Altogether, 13 biomarkers were identified. The dose-response curve based on nine important biomarkers indicated that doses in the 0.42-6.61 g/kg range (EC20-EC80 range, corresponding to 4.00-62.95 g in the clinic) were effective for cholestasis treatment. The pathway analysis showed that bile acid metabolism and excretion, inflammation and amino acid metabolism were altered by rhubarb in a dose-dependent manner and might be involved in the dose-response relationship and therapeutic mechanism of rhubarb for cholestasis treatment.
Keywords: cholestasis; dose response; metabolomics; pathway analysis; rhubarb.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

