Emerging status of anaplasmosis in cattle in Hisar
- PMID: 27065645
- PMCID: PMC4825280
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.768-771
Emerging status of anaplasmosis in cattle in Hisar
Abstract
Aim: Anaplasma marginale is a rickettsial pathogen responsible for progressive anemia in ruminants leading to huge economic losses. The objectives of this cross-sectional study were to determine the prevalence of anaplasmosis and therapeutic evaluation of traditional line of treatment.
Materials and methods: A total of 168 cattle presented to Teaching Veterinary Clinical Complex, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary & Animal Sciences, Hisar during the period of 3 months (July-September, 2014) with history of fever, anorexia, reduced milk yield and tick infestation were analyzed for prevalence of hemoprotozoan diseases using classical giemsa stained thin blood smear parasitological method.
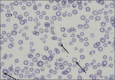
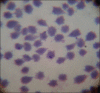
Results: Out of these 168 animals, 7 (4.17%) were found to be suffering from anaplasmosis on the basis of presence of dense, rounded, intra-erythrocytic bodies situated on or near the margin of the erythrocytes. Overall prevalence of theileriosis and babesiosis were found to be 42.9% and 1.8%, respectively. Level of parasitemia was noticed to be 1.2%, 0.8% and 0.9% in babesiosis, theileriosis, and anaplasmosis, respectively. The most marked and common clinical signs reported in all the cases were severe anemia (hemoglobin=3-6 g/dl) and history of fever, followed by normal body temperature. Following treatment with oxytetracycline parenterally along with supportive therapy out of seven cases six got recovered without any side-effects.
Conclusion: The current study indicates the emerging status of anaplasmosis in this part of the country as during the past few years there are very few reports showing the prevalence of clinical cases of anaplasmosis. Treatment with oxytetracycline yielded excellent result showing recovery in most of the clinical cases.
Keywords: anaplasmosis; giemsa staining; hemoprotozoan; oxytetracycline.
Figures
References
-
- Marchette N, Stiller D. The anaplasmataceae Bartonellaceae and Rochalimaea quintana. In: Marchette N.J, editor. Ecological Relationships and Evolution in the Rickettsiae. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press; 1982. pp. 98–106.
-
- Kocan K.M, De La Fuente J, Blouin E.F, Garica-Garcia J.C. Anaplasma marginale (Rickettsiales:Anaplasmataceae):Recent advances in defining host-pathogen adaptations of a tick-borne rickettsia. Parasitology. 2004;129:285–300. - PubMed
-
- Jongejan F, Uilenberg G. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology. 2004;129:S3–S14. - PubMed
-
- Aubry P, Geale D.W. A review of bovine anaplasmosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011;58(1):1–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous