Flexible Distributed Pressure Sensing Strip for a Urethral Catheter
- PMID: 27065719
- PMCID: PMC4824413
- DOI: 10.1109/JMEMS.2015.2444992
Flexible Distributed Pressure Sensing Strip for a Urethral Catheter
Abstract
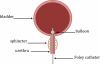
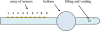
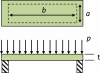
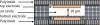
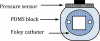
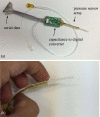
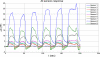
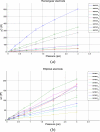
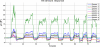
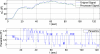
A multi-sensor flexible strip is developed for a urethral catheter to measure distributed pressure in a human urethra. The developed sensor strip has important clinical applications in urodynamic testing for analyzing the causes of urinary incontinence in patients. There are two major challenges in the development of the sensor. First, a highly sensitive sensor strip that is flexible enough for urethral insertion into a human body is required and second, the sensor has to work reliably in a liquid in-vivo environment in the human body. Capacitive force sensors are designed and micro-fabricated using polyimide/PDMS substrates and copper electrodes. To remove the parasitic influence of urethral tissues which create fringe capacitance that can lead to significant errors, a reference fringe capacitance measurement sensor is incorporated on the strip. The sensing strip is embedded on a catheter and experimental in-vitro evaluation is presented using a bench-top pressure chamber. The sensors on the strip are able to provide the required sensitivity and range. Preliminary experimental results also show promise that by using measurements from the reference parasitic sensor on the strip, the influence of parasitics from human tissue on the pressure measurements can be removed.
Keywords: capacitive sensors; catheter pressure sensors; in vivo force sensors; in vivo sensors; instrumented catheter; parasitic capacitance; urethral sensors.
Figures









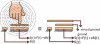

References
-
- Abrams P, et al. The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function recommended by the international continence society. International Urogynecology Journal. 1990;1(1):45–58.
-
- Bo K. Urinary incontinence, pelvic floor dysfunction, exercise and sport. Sports Med. 2004;34(7):451–64. - PubMed
-
- Nygaard I, et al. Is urinary incontinence a barrier to exercise in women? Obstet Gynecol. 2005;106(2):307–14. - PubMed
-
- Schulman C, Claesm H, Mattijs J. Urinary incontinence in Belgium: a population based epidemiological survey. Euro Urol. 1997;32:315. - PubMed
-
- Herzog AR, Fultz NH. Prevalence and incidence of urinary incontinence in community-dwelling populations. J. Am. Geriat. Soc. 1990;38:273. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
