An enhanced algorithm for multiple sequence alignment of protein sequences using genetic algorithm
- PMID: 27065770
- PMCID: PMC4820728
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2015-302
An enhanced algorithm for multiple sequence alignment of protein sequences using genetic algorithm
Abstract
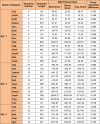
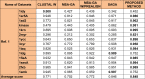
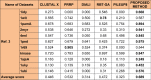
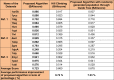
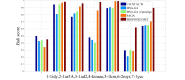
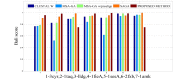
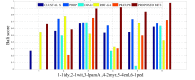
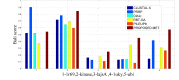
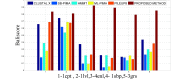
One of the most fundamental operations in biological sequence analysis is multiple sequence alignment (MSA). The basic of multiple sequence alignment problems is to determine the most biologically plausible alignments of protein or DNA sequences. In this paper, an alignment method using genetic algorithm for multiple sequence alignment has been proposed. Two different genetic operators mainly crossover and mutation were defined and implemented with the proposed method in order to know the population evolution and quality of the sequence aligned. The proposed method is assessed with protein benchmark dataset, e.g., BALIBASE, by comparing the obtained results to those obtained with other alignment algorithms, e.g., SAGA, RBT-GA, PRRP, HMMT, SB-PIMA, CLUSTALX, CLUSTAL W, DIALIGN and PILEUP8 etc. Experiments on a wide range of data have shown that the proposed algorithm is much better (it terms of score) than previously proposed algorithms in its ability to achieve high alignment quality.
Keywords: bioinformatics; crossover operator; genetic algorithm; multiple sequence alignment; mutation operator.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Vertical decomposition with Genetic Algorithm for Multiple Sequence Alignment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Aug 25;12:353. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-353. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21867510 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing multiple sequence alignments using a genetic algorithm based on three objectives: structural information, non-gaps percentage and totally conserved columns.Bioinformatics. 2013 Sep 1;29(17):2112-21. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt360. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23793754
-
A Novel Approach to Multiple Sequence Alignment Using Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Decomposition.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016 Mar;20(2):717-27. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2015.2403397. Epub 2015 Feb 12. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016. PMID: 25700475
-
An approach for COFFEE objective function to global DNA multiple sequence alignment.Comput Biol Chem. 2018 Aug;75:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.04.012. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Comput Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29738913
-
Performance assessment of protein multiple sequence alignment algorithms based on permutation similarity measurement.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Sep 3;399(4):470-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.103. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20678477 Review.
References
-
- Ankit A, Huang X. Pairwise statistical significance of local sequence alignment using substitution matrices with sequence-pair-specific distance. Proc Int Conf Inform Technol. 2008:94–99.
-
- Auyeung A, Melcher U. Evaluations of protein sequence alignments using structural information. Int Conf Inform Technol: Coding and Computing. 2005;2:748–749.
-
- Bhattacharjee A, Sultana KZ, Shams Z. Dynamic and parallel approaches to optimal evolutionary tree construction. Can Conf Electr Comp Engin. 2006:119–112.
-
- Blackshields G, Wallace IM, Larkin M, Higgins DG. Analysis and comparison of benchmarks for multiple sequence alignment. In Silico Biol. 2006;6:321–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
