Sub-MIC Tylosin Inhibits Streptococcus suis Biofilm Formation and Results in Differential Protein Expression
- PMID: 27065957
- PMCID: PMC4811924
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00384
Sub-MIC Tylosin Inhibits Streptococcus suis Biofilm Formation and Results in Differential Protein Expression
Abstract
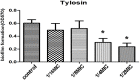
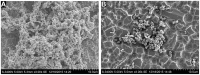
Streptococcus suis (S.suis) is an important zoonotic pathogen that causes severe diseases in humans and pigs. Biofilms of S. suis can induce persistent infections that are difficult to treat. In this study, the effect of tylosin on biofilm formation of S. suis was investigated. 1/2 minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and 1/4 MIC of tylosin were shown to inhibit S. suis biofilm formation in vitro. By using the iTRAQ strategy, we compared the protein expression profiles of S. suis grown with sub-MIC tylosin treatment and with no treatment. A total of 1501 proteins were identified by iTRAQ. Ninety-six differentially expressed proteins were identified (Ratio > ±1.5, p < 0.05). Several metabolism proteins (such as phosphoglycerate kinase) and surface proteins (such as ABC transporter proteins) were found to be involved in biofilm formation. Our results indicated that S. suis metabolic regulation, cell surface proteins, and virulence proteins appear to be of importance in biofilm growth with sub-MIC tylosin treatment. Thus, our data revealed the rough regulation of biofilm formation that may provide a foundation for future research into mechanisms and targets.
Keywords: S. suis; biofilms; iTRAQ; proteomics; tylosin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of sub-MIC erythromycin inhibiting biofilm formation of S. suis in vitro.J Proteomics. 2015 Feb 26;116:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.12.019. Epub 2015 Jan 9. J Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25579403
-
Analysis of multidrug resistance in Streptococcus suis ATCC 700794 under tylosin stress.Virulence. 2019 Dec;10(1):58-67. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1557505. Virulence. 2019. PMID: 31874073 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-Inhibitory Concentrations of Amoxicillin and Tylosin Affect the Biofilm Formation and Virulence of Streptococcus suis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 8;19(14):8359. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148359. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35886209 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance related to biofilm formation in Streptococcus suis.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Oct;104(20):8649-8660. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10873-9. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32897417 Review.
-
Streptococcus suis biofilm: regulation, drug-resistance mechanisms, and disinfection strategies.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Nov;102(21):9121-9129. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9356-z. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30209548 Review.
Cited by
-
Rational Proteomic Analysis of a New Domesticated Klebsiella pneumoniae x546 Producing 1,3-Propanediol.Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 26;12:770109. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.770109. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34899654 Free PMC article.
-
Maximum levels of cross-contamination for 24 antimicrobial active substances in non-target feed. Part 6: Macrolides: tilmicosin, tylosin and tylvalosin.EFSA J. 2021 Oct 26;19(10):e06858. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6858. eCollection 2021 Oct. EFSA J. 2021. PMID: 34729086 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Proteomic Analysis Provides insight into the Key Proteins as Possible Targets Involved in Aspirin Inhibiting Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus xylosus.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 21;8:543. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00543. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28871227 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomic investigation unravels the pathobiology of Mycobacterium fortuitum biofilm.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;107(19):6029-6046. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12705-y. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37542577
-
Role of hsp20 in the Production of Spores and Insecticidal Crystal Proteins in Bacillus thuringiensis.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 4;10:2059. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02059. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31551991 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

