Circulating Human Neonatal Naïve B Cells are Deficient in CD73 Impairing Purine Salvage
- PMID: 27066009
- PMCID: PMC4812068
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00121
Circulating Human Neonatal Naïve B Cells are Deficient in CD73 Impairing Purine Salvage
Abstract
Background: Extracellular purines, in particular adenosine (Ado) and adenosine-triphosphate, are critical immunoregulatory molecules. Expression and activity of purine ecto-enzymes on B cells in neonatal and adult blood may influence their function and has been incompletely characterized.
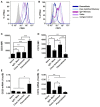
Methods: Mononuclear cells were isolated from human neonatal (cord blood) or adult (peripheral blood) subjects and evaluated directly by flow cytometry for expression of purine ecto-enzymes. Additionally, B cell subsets were isolated from mononuclear cell fractions by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and gene transcription of purine ecto-enzymes (CD39 and CD73), Ado deaminase (ADA1), purine nucleoside phosphorylase, and select purine receptors (A2a) were evaluated by reverse transcription followed by qRT-PCR. Immuno-magnetic-bead isolated naïve B cells were evaluated for enzymatic activity by incubation with radio-labeled purines followed by thin-layer chromatography, and subsequent B cell Ado acquisition was evaluated by liquid scintillation quantitation of radio-labeled Ado uptake.
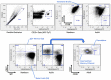
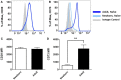
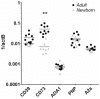
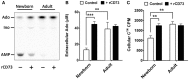
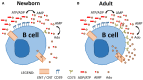
Results: Relative to their adult counterparts, neonatal circulating naïve B cells were markedly and selectively deficient in CD73 as observed by gene transcription, surface protein expression, and enzyme activity. Neonatal naïve B cell deficiency of CD73 expression significantly impaired their capacity to acquire extracellular purines for purine salvage.
Conclusion: Human neonatal circulating naïve B cells are selectively deficient in CD73, impairing extracellular purine acquisition and potentially contributing to impaired B cell responses in early life.
Keywords: B cells; CD73; adenosine; neonatal; purine; purinergic; salvage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The evidence for two opposite, ATP-generating and ATP-consuming, extracellular pathways on endothelial and lymphoid cells.Biochem J. 2002 Oct 1;367(Pt 1):121-8. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020439. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12099890 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical and functional analysis of ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 (CD39) and ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73) in pig aortic valves.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2014;33(4-6):305-12. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2014.885985. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2014. PMID: 24940684
-
Ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 enhances endothelial barrier function and sprouting in blood but not lymphatic vasculature.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Feb;45(2):562-73. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444856. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25402681
-
Enzymes involved in metabolism of extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides: functional implications and measurement of activities.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Nov-Dec;49(6):473-97. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2014.953627. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25418535 Review.
-
Nucleotide- and nucleoside-converting ectoenzymes: Important modulators of purinergic signalling cascade.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 May;1783(5):673-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.024. Epub 2008 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18302942 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting CD73 to augment cancer immunotherapy.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;53:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32777746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding Antibody Responses in Early Life: Baby Steps towards Developing an Effective Influenza Vaccine.Viruses. 2021 Jul 17;13(7):1392. doi: 10.3390/v13071392. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34372597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Life HIV-1 Immunization: Providing a Window for Protection Before Sexual Debut.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2018 Oct;34(10):823-827. doi: 10.1089/AID.2018.0018. Epub 2018 Jul 3. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2018. PMID: 29860868 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Early-Life Adaptive Immunity to Guide Interventions for Pediatric Health.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 21;11:595297. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.595297. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33552052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neonatal immune response to rhinovirus A16 has diminished dendritic cell function and increased B cell activation.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 18;12(10):e0180664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180664. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29045416 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

