Effects of Armolipid Plus on small dense LDL particles in a sample of patients affected by familial combined hyperlipidemia
- PMID: 27066111
- PMCID: PMC4821502
- DOI: 10.2217/clp.15.37
Effects of Armolipid Plus on small dense LDL particles in a sample of patients affected by familial combined hyperlipidemia
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to test small dense LDL changes with Armolipid Plus treatment in patients with familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCHL).
Methods: After 4 weeks, 30 patients with FCHL were included in an 8-week, randomized, double-blind study and were taking, in addition to the standard diet, either placebo or Armolipid Plus.
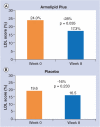
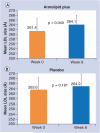
Results: The placebo group showed no statistically significant differences in the studied parameters; instead, in the Armolipid Plus group, statistically significant reduction differences were detected in BMI (p = 0.010), LDL score (p = 0.035) and an increase in mean LDL particle diameter (p = 0.040).
Conclusion: The combination of a standard diet with Armolipid Plus is able to reduce LDL score and increase LDL particle diameter in a group of FCHL after 8 weeks of treatment.
Keywords: Armolipid Plus; familial combined hyperlipidemia; small dense LDL.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Armolipid Plus®: An Updated PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 16;13(2):638. doi: 10.3390/nu13020638. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33669333 Free PMC article.
-
A nutraceutical approach (Armolipid Plus) to reduce total and LDL cholesterol in individuals with mild to moderate dyslipidemia: Review of the clinical evidence.Atheroscler Suppl. 2017 Feb;24:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosissup.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Dec 18. Atheroscler Suppl. 2017. PMID: 27998714 Review.
-
Three arms, double-blind, non-inferiority, randomized clinical study testing the lipid-lowering effect of a novel dietary supplement containing red yeast rice and artichoke extracts compared to Armolipid Plus® and placebo.Arch Med Sci. 2023 Jun 17;19(5):1169-1179. doi: 10.5114/aoms/167969. eCollection 2023. Arch Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37732047 Free PMC article.
-
LDL physical and chemical properties in familial combined hyperlipidemia.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):452-9. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.4.452. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995. PMID: 7749856
-
Effect of statins on LDL particle size in patients with familial combined hyperlipidemia: a comparison between atorvastatin and pravastatin.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2005 Feb;15(1):47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2004.08.001. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2005. PMID: 15871851 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Beneficial Effects of a Nutraceutical Combination on Lipid Profiles in Children with Moderate and Severe Hypercholesterolemia.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 16;14(12):1608. doi: 10.3390/biom14121608. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766315 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Armolipid Plus®: An Updated PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 16;13(2):638. doi: 10.3390/nu13020638. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33669333 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical-Based Approaches for Cardiovascular Diseases Prevention Targeting Atherogenic Small Dense LDL.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 9;14(4):825. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040825. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Monacolin K and COQ10 supplementation in hypertensive and hypercholesterolemic subjects with metabolic syndrome.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Sep;105:992-996. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.076. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30021394 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The beneficial effects of nutraceuticals and natural products on small dense LDL levels, LDL particle number and LDL particle size: a clinical review.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Apr 11;19(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01250-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32276631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Greevenbroek MM, Stalenhoef AF, de Graaf J, Brouwers MC. Familial combined hyperlipidemia: from molecular insights to tailored therapy. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2014;25:176–182. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins PN, Heiss G, Ellison RC, et al. Coronary artery disease risk in familial combined hyperlipidemia and familial hypertriglyceridemia: a case–control comparison from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Family Heart Study. Circulation. 2003;108:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Pauciullo P, Gentile M, Marotta G, et al. Small dense low-density lipoprotein in familial combined hyperlipidemia: independent of metabolic syndrome and related to history of cardiovascular events. Atherosclerosis. 2009;203:320–324. [This paper reported association between LDL score and familial combined hyperlipidemia.] - PubMed
-
- Mykkanen L, Kuusisto J, Haffner SM, Laakso M, Austin MA. LDL size and risk of coronary heart disease in elderly men and women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999;19:2742–2748. - PubMed
-
- Austin MA, Breslow JL, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Willett WC, Krauss RM. Low-density lipoprotein subclass patterns and risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1988;260:1917–1921. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources