Discovery of a highly potent glucocorticoid for asthma treatment
- PMID: 27066265
- PMCID: PMC4822341
- DOI: 10.1038/celldisc.2015.35
Discovery of a highly potent glucocorticoid for asthma treatment
Abstract
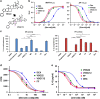
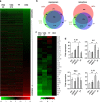
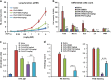
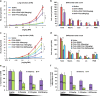
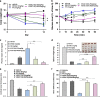
Glucocorticoids are the most effective treatment for asthma. However, their clinical applications are limited by low efficacy in severe asthma and by undesired side effects associated with high dose or prolonged use. The most successful approach to overcome these limitations has been the development of highly potent glucocorticoids that can be delivered to the lungs by inhalation to achieve local efficacy with minimal systemic effects. On the basis of our previous structural studies, we designed and developed a highly potent glucocorticoid, VSGC12, which showed an improved anti-inflammation activity in both cell-based reporter assays and cytokine inhibition experiments, as well as in a gene expression profiling of mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells. In a mouse asthma model, VSGC12 delivered a higher efficacy than fluticasone furoate, a leading clinical compound, in many categories including histology and the number of differentiated immune cells. VSGC12 also showed a higher potency than fluticasone furoate in repressing most asthma symptoms. Finally, VSGC12 showed a better side effect profile than fluticasone furoate at their respective effective doses, including better insulin response and less bone loss in an animal model. The excellent therapeutic and side effect properties of VSGC12 provide a promising perspective for developing this potent glucocorticoid as a new effective drug for asthma.
Keywords: Glucocorticoids; VSGC12; asthma; glucocorticoid receptor; potency.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of highly potent glucocorticoids for steroid-resistant severe asthma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 2;116(14):6932-6937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816734116. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30894497 Free PMC article.
-
Fluticasone furoate/vilanterol: a review of its use in patients with asthma.Drugs. 2015 Mar;75(4):407-18. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0354-5. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25648266 Review.
-
Mometasone furoate: an inhaled glucocorticoid for the management of asthma in adults and children.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009 Aug;10(12):2009-14. doi: 10.1517/14656560903078428. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19618993 Review.
-
In vitro glucocorticoid receptor binding and transcriptional activation by topically active glucocorticoids.Arzneimittelforschung. 1998 Sep;48(9):956-60. Arzneimittelforschung. 1998. PMID: 9793625
-
Inhaled mometasone furoate: a review of its use in adults and adolescents with persistent asthma.Drugs. 2001;61(9):1325-50. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161090-00011. Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11511026 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into glucocorticoid receptor function.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Nov 1;49(5):2333-2343. doi: 10.1042/BST20210419. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34709368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Channel Expansion in the Ligand-Binding Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Contributes to the Activity of Highly Potent Glucocorticoid Analogues.Molecules. 2024 Mar 29;29(7):1546. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071546. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611825 Free PMC article.
-
Development of highly potent glucocorticoids for steroid-resistant severe asthma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 2;116(14):6932-6937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816734116. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30894497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holgate ST . A look at the pathogenesis of asthma: the need for a change in direction. Discov Med 2010; 9: 439–447. - PubMed
-
- AAAAI Asthma Statistics. http://www.aaaai.org/about-the-aaaai/newsroom/asthma-statistics.aspx.
-
- CDC Asthma in the US. http://www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/asthma/.
-
- Tamm M , Richards DH , Beghe B , Fabbri L . Inhaled corticosteroid and long-acting beta2-agonist pharmacological profiles: effective asthma therapy in practice. Respir Med 2012; 106 (Suppl 1): S9–19. - PubMed
-
- Holgate ST , Polosa R . The mechanisms, diagnosis, and management of severe asthma in adults. Lancet 2006; 368: 780–793. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

