THink: Inferring Cognitive Status from Subtle Behaviors
- PMID: 27066307
- PMCID: PMC4825804
THink: Inferring Cognitive Status from Subtle Behaviors
Abstract
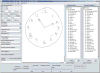
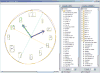
The Digital Clock Drawing Test is a fielded application that provides a major advance over existing neuropsychological testing technology. It captures and analyzes high precision information about both outcome and process, opening up the possibility of detecting subtle cognitive impairment even when test results appear superficially normal. We describe the design and development of the test, document the role of AI in its capabilities, and report on its use over the past seven years. We outline its potential implications for earlier detection and treatment of neurological disorders. We also set the work in the larger context of the THink project, which is exploring multiple approaches to determining cognitive status through the detection and analysis of subtle behaviors.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 2012;8(2):2012. - PubMed
-
- Freedman M, Leach L, Kaplan E, Winocur G, Shulman K, Delis D. Clock Drawing: A Neuro-psychological Analysis. Oxford Univ Press; 1994.
-
- Fryer S, Sutton E, Tiplady B, Wright P. Trail making without trails: the use of a pen computer task for assessing brain damage. Clinical Neuropsychology Assessment. 2000;2:151–165.
-
- Grande L, Rudolph J, Davis R, Penney D, Price C, Swenson R, Libon D, Milberg W. Clock Drawing: Standing the Test of Time. In: Ashendorf, Swenson, Libon, editors. The Boston Process Approach to Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford Univ Press; 2013. 2013.
-
- Kim H. PhD, Thesis. Georgia Institute of Technology, College of Computing; 2013. The Clockme System: Computer-Assisted Screening Tool For Dementia. 2013.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous