Genetic analysis for a shared biological basis between migraine and coronary artery disease
- PMID: 27066539
- PMCID: PMC4821079
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000010
Genetic analysis for a shared biological basis between migraine and coronary artery disease
Abstract
Objective: To apply genetic analysis of genome-wide association data to study the extent and nature of a shared biological basis between migraine and coronary artery disease (CAD).
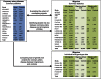
Methods: Four separate methods for cross-phenotype genetic analysis were applied on data from 2 large-scale genome-wide association studies of migraine (19,981 cases, 56,667 controls) and CAD (21,076 cases, 63,014 controls). The first 2 methods quantified the extent of overlapping risk variants and assessed the load of CAD risk loci in migraineurs. Genomic regions of shared risk were then identified by analysis of covariance patterns between the 2 phenotypes and by querying known genome-wide significant loci.
Results: We found a significant overlap of genetic risk loci for migraine and CAD. When stratified by migraine subtype, this was limited to migraine without aura, and the overlap was protective in that patients with migraine had a lower load of CAD risk alleles than controls. Genes indicated by 16 shared risk loci point to mechanisms with potential roles in migraine pathogenesis and CAD, including endothelial dysfunction (PHACTR1) and insulin homeostasis (GIP).
Conclusions: The results suggest that shared biological processes contribute to risk of migraine and CAD, but surprisingly this commonality is restricted to migraine without aura and the impact is in opposite directions. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these processes and their opposite relationship to migraine and CAD may improve our understanding of both disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013;33:629–808. - PubMed
-
- Charles AC, Baca SM. Cortical spreading depression and migraine. Nat Rev Neurol 2013;9:637–644. - PubMed
-
- Charles A. Migraine is not primarily a vascular disorder. Cephalalgia 2012;32:431–432. - PubMed
-
- Ashina M. Vascular changes have a primary role in migraine. Cephalalgia 2012;32:428–430. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- RC2 MH089951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081802/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G1002319/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AA009203/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K05 AA000145/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 MH083268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA012502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH068457/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS061836/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AA015416/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
