Late-onset Alzheimer disease risk variants mark brain regulatory loci
- PMID: 27066552
- PMCID: PMC4807909
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000012
Late-onset Alzheimer disease risk variants mark brain regulatory loci
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the top late-onset Alzheimer disease (LOAD) risk loci detected or confirmed by the International Genomics of Alzheimer's Project for association with brain gene expression levels to identify variants that influence Alzheimer disease (AD) risk through gene expression regulation.
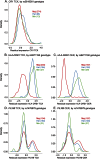
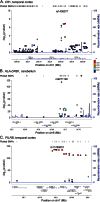
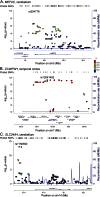
Methods: Expression levels from the cerebellum (CER) and temporal cortex (TCX) were obtained using Illumina whole-genome cDNA-mediated annealing, selection, extension, and ligation assay (WG-DASL) for ∼400 autopsied patients (∼200 with AD and ∼200 with non-AD pathologies). We tested 12 significant LOAD genome-wide association study (GWAS) index single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for cis association with levels of 34 genes within ±100 kb. We also evaluated brain levels of 14 LOAD GWAS candidate genes for association with 1,899 cis-SNPs. Significant associations were validated in a subset of TCX samples using next-generation RNA sequencing (RNAseq).
Results: We identified strong associations of brain CR1, HLA-DRB1, and PILRB levels with LOAD GWAS index SNPs. We also detected other strong cis-SNPs for LOAD candidate genes MEF2C, ZCWPW1, and SLC24A4. MEF2C and SLC24A4, but not ZCWPW1 cis-SNPs, also associate with LOAD risk, independent of the index SNPs. The TCX expression associations could be validated with RNAseq for CR1, HLA-DRB1, ZCWPW1, and SLC24A4.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that some LOAD GWAS variants mark brain regulatory loci, nominate genes under regulation by LOAD risk variants, and annotate these variants for their brain regulatory effects.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
