Atypical parkinsonism caused by Pro105Leu mutation of prion protein: A broad clinical spectrum
- PMID: 27066585
- PMCID: PMC4817902
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000048
Atypical parkinsonism caused by Pro105Leu mutation of prion protein: A broad clinical spectrum
Abstract
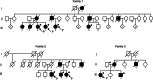
Objective: To delineate molecular and clinical characteristics of 3 families with PRNP P105L mutation, a variant of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome whose main motor symptoms were parkinsonism and/or involuntary movements.
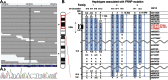
Methods: The causative mutation was first determined in the affected patients of family 1 using whole-exome sequencing, and then mutational analysis was extended to families 2 and 3. The clinical features of the patients of these 3 families were summarized. Haplotype analysis was performed using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism array.
Results: The whole-exome sequencing revealed that the heterozygous mutation c.314C>T (p.P105L) in PRNP was the only known pathogenic mutation shared by the 3 patients of the family with autosomal dominant parkinsonism. We further identified the same mutation in patients of the other 2 families with autosomal dominant parkinsonism and/or involuntary movements. The clinical features of our patients with PRNP P105L mutation included various motor symptoms such as parkinsonism and involuntary movements in addition to progressive dementia. The clinical features in part overlapped with those of other forms of inherited prion diseases, such as fatal familial insomnia and Huntington disease-like type 1. The patients with PRNP P105L mutation shared a haplotype spanning 7.1 Mb around PRNP, raising the possibility that the mutations in the patients originated from a common founder.
Conclusion: Most of the patients presented with parkinsonism in addition to progressive dementia. Although spastic paraparesis has been emphasized as the main clinical feature, the clinical spectrum of patients with PRNP P105L is broader than expected.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prion disease.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;148:441-464. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64076-5.00029-6. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29478593 Review.
-
Specific amyloid-β42 deposition in the brain of a Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease patient with a P105L mutation on the prion protein gene.Prion. 2018;12(5-6):315-319. doi: 10.1080/19336896.2018.1541689. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Prion. 2018. PMID: 30394185 Free PMC article.
-
A novel PRNP-P105S mutation associated with atypical prion disease and a rare PrPSc conformation.Neurology. 2008 Oct 28;71(18):1431-8. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000330237.94742.fa. Neurology. 2008. PMID: 18955686 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations of the prion protein gene phenotypic spectrum.J Neurol. 2002 Nov;249(11):1567-82. doi: 10.1007/s00415-002-0896-9. J Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12420099
-
[Genetic background of human prion diseases].Ideggyogy Sz. 2007 Nov 30;60(11-12):438-46. Ideggyogy Sz. 2007. PMID: 18198790 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Alterations of Striatal Subregions in a Prion Protein Gene V180I Mutation Carrier Presented as Frontotemporal Dementia With Parkinsonism.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 15;14:830602. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.830602. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35493933 Free PMC article.
-
Prion Mutations in Republic of Republic of Korea, China, and Japan.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):625. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010625. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An autopsy report of three kindred in a Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease P105L family with a special reference to prion protein, tau, and beta-amyloid.Brain Behav. 2018 Oct;8(10):e01117. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1117. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 30240140 Free PMC article.
-
Serial changes in regional cerebral blood flow in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease caused by a Pro-to-Leu mutation at codon 105 in the prion protein gene.Prion. 2023 Dec;17(1):138-140. doi: 10.1080/19336896.2023.2256928. Prion. 2023. PMID: 37705331 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of neurodegenerative diseases.Neurol Genet. 2016 Feb 18;2(1):e52. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000052. eCollection 2016 Feb. Neurol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27066589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iwasaki Y, Kizawa M, Hori N, Kitamoto T, Sobue G. A case of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome with the P105L prion protein gene mutation presenting with ataxia and extrapyramidal signs without spastic paraparesis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2009;111:606–609. - PubMed
-
- Yamada M, Itoh Y, Fujigasaki H, et al. A missense mutation at codon 105 with codon 129 polymorphism of the prion protein gene in a new variant of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. Neurology 1993;43:2723–2724. - PubMed
-
- Kitamoto T, Amano N, Terao Y, et al. A new inherited prion disease (PrP-P105L mutation) showing spastic paraparesis. Ann Neurol 1993;34:808–813. - PubMed
-
- Shiraishi A, Mizusawa H, Yamada M. Early and persistent sensory-psychiatric symptoms in an inherited prion disease with a PrP P105L mutation. J Neurol 2002;249:1740–1741. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
