FNDC4 acts as an anti-inflammatory factor on macrophages and improves colitis in mice
- PMID: 27066907
- PMCID: PMC4832079
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11314
FNDC4 acts as an anti-inflammatory factor on macrophages and improves colitis in mice
Abstract
FNDC4 is a secreted factor sharing high homology with the exercise-associated myokine irisin (FNDC5). Here we report that Fndc4 is robustly upregulated in several mouse models of inflammation as well as in human inflammatory conditions. Specifically, FNDC4 levels are increased locally at inflamed sites of the intestine of inflammatory bowel disease patients. Interestingly, administration of recombinant FNDC4 in the mouse model of induced colitis markedly reduces disease severity compared with mice injected with a control protein. Conversely, mice lacking Fndc4 develop more severe colitis. Analysis of binding of FNDC4 to different immune cell types reveals strong and specific binding to macrophages and monocytes. FNDC4 treatment of bone marrow-derived macrophages in vitro results in reduced phagocytosis, increased cell survival and reduced proinflammatory chemokine expression. Hence, treatment with FNDC4 results in a state of dampened macrophage activity, while enhancing their survival. Thus, we have characterized FNDC4 as a factor with direct therapeutic potential in inflammatory bowel disease and possibly other inflammatory diseases.
Figures
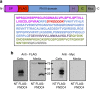
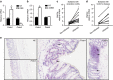
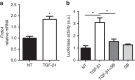
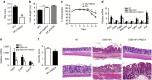
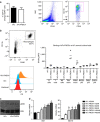
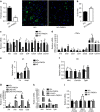
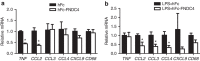
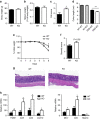
References
-
- Molodecky N. A. et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology 142, 46–54 e42 quiz e30 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Podolsky D. K. Inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 347, 417–429 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Teufel A., Malik N., Mukhopadhyay M. & Westphal H. Frcp1 and Frcp2, two novel fibronectin type III repeat containing genes. Gene 297, 79–83 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

