HPF1/C4orf27 Is a PARP-1-Interacting Protein that Regulates PARP-1 ADP-Ribosylation Activity
- PMID: 27067600
- PMCID: PMC4858568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.03.008
HPF1/C4orf27 Is a PARP-1-Interacting Protein that Regulates PARP-1 ADP-Ribosylation Activity
Abstract
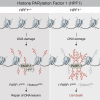
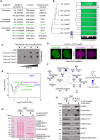
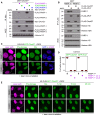
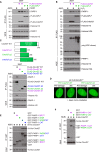
We report the identification of histone PARylation factor 1 (HPF1; also known as C4orf27) as a regulator of ADP-ribosylation signaling in the DNA damage response. HPF1/C4orf27 forms a robust protein complex with PARP-1 in cells and is recruited to DNA lesions in a PARP-1-dependent manner, but independently of PARP-1 catalytic ADP-ribosylation activity. Functionally, HPF1 promotes PARP-1-dependent in trans ADP-ribosylation of histones and limits DNA damage-induced hyper-automodification of PARP-1. Human cells lacking HPF1 exhibit sensitivity to DNA damaging agents and PARP inhibition, thereby suggesting an important role for HPF1 in genome maintenance and regulating the efficacy of PARP inhibitors. Collectively, our results demonstrate how a fundamental step in PARP-1-dependent ADP-ribosylation signaling is regulated and suggest that HPF1 functions at the crossroads of histone ADP-ribosylation and PARP-1 automodification.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ahel I., Ahel D., Matsusaka T., Clark A.J., Pines J., Boulton S.J., West S.C. Poly(ADP-ribose)-binding zinc finger motifs in DNA repair/checkpoint proteins. Nature. 2008;451:81–85. - PubMed
-
- Barkauskaite E., Jankevicius G., Ahel I. Structures and mechanisms of enzymes employed in the synthesis and degradation of PARP-dependent protein ADP-ribosylation. Mol. Cell. 2015;58:935–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

