Homing to solid cancers: a vascular checkpoint in adoptive cell therapy using CAR T-cells
- PMID: 27068943
- PMCID: PMC5264496
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20150254
Homing to solid cancers: a vascular checkpoint in adoptive cell therapy using CAR T-cells
Abstract
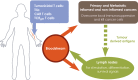
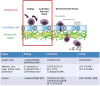
The success of adoptive T-cell therapies for the treatment of cancer patients depends on transferred T-lymphocytes finding and infiltrating cancerous tissues. For intravenously transferred T-cells, this means leaving the bloodstream (extravasation) from tumour blood vessels. In inflamed tissues, a key event in extravasation is the capture, rolling and arrest of T-cells inside blood vessels which precedes transmigration across the vessel wall and entry into tissues. This depends on co-ordinated signalling of selectins, integrins and chemokine receptors on T-cells by their respective ligands which are up-regulated on inflamed blood vessels. Clinical data and experimental studies in mice suggest that tumour blood vessels are anergic to inflammatory stimuli and the recruitment of cytotoxic CD8(+)T-lymphocytes is not very efficient. Interestingly, and somewhat counter-intuitively, anti-angiogenic therapy can promote CD8(+)T-cell infiltration of tumours and increase the efficacy of adoptive CD8(+)T-cell therapy. Rather than inhibit tumour angiogenesis, anti-angiogenic therapy 'normalizes' (matures) tumour blood vessels by promoting pericyte recruitment, increasing tumour blood vessel perfusion and sensitizing tumour blood vessels to inflammatory stimuli. A number of different approaches are currently being explored to increase recruitment by manipulating the expression of homing-associated molecules on T-cells and tumour blood vessels. Future studies should address whether these approaches improve the efficacy of adoptive T-cell therapies for solid, vascularized cancers in patients.
Keywords: chemokine receptors; endothelial cell anergy; extravasation; high endothelial venules; homing; integrins; selectins; tumour blood vessels; tumouricidal T-lymphocytes; vessel normalization.
© 2016 Authors; published by Portland Press Limited.
Figures

References
-
- Galon J., Costes A., Sanchez-Cabo F., Kirilovsky A., Mlecnik B., Lagorce-Pages C., Tosolini M., Camus M., Berger A., Wind P., et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006;313:1960–1964. doi: 10.1126/science.1129139. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martinet L., Garrido I., Filleron T., Le Guellec S., Bellard E., Fournie J.J., Rochaix P., Girard J.P. Human solid tumors contain high endothelial venules: association with T- and B-lymphocyte infiltration and favorable prognosis in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:5678–5687. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0431. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dudley M.E., Wunderlich J.R., Robbins P.F., Yang J.C., Hwu P., Schwartzentruber D.J., Topalian S.L., Sherry R., Restifo N.P., Hubicki A.M., et al. Cancer regression and autoimmunity in patients after clonal repopulation with antitumor lymphocytes. Science. 2002;298:850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.1076514. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

