Der f 21, a novel allergen from dermatophagoides farina
- PMID: 27069539
- PMCID: PMC4759415
Der f 21, a novel allergen from dermatophagoides farina
Abstract
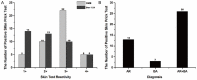
The Dermatophagoides farina (D. farina) allergens are an important factor contributing to allergic disease. To identify new allergens is important for diagnosis and treatment of allergic diseases. In this study, we sought to characterize the biological activity of Der f 21 of D. farina. The recombinant Der f 21 protein was characterized by western-blot, ELISA and Skin prick test using clinic patient's serum.An allergic asthma mouse model was established with the rDer f 21 as a specific antigen. The results showed that the sera from 28.9% in 38 dust mite allergic children displayed positive results in response to rDer f 21, and 42% in 98 dust mite allergic patients displayed positive response in skin prick test. In addition, Immune inhibition assays showed there was IgE cross-reactivity between rDer f 21 and rDer f 5. Moreover, an allergic asthma mouse model was established. Airway hyperresponsiveness, serum specific IgE, IgG1, eosinophil infiltration in the allergic mice, interleukin-4(IL-4) and interferon-γ (INF-γ) from spleen cells were markedly increased in the allergic mice. The results demonstrate that Der f 21 is a novel allergen.
Keywords: Allergen; Der f 21; airway; biological activity; dust mite.
Figures





References
-
- Cheng L, Chen YZ. [Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) achievements in 10 years and future needs] . Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;47:619–622. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Wang H, Chen Y, Zheng J, Wong GW, Zhong N. House dust mite sensitization is the main risk factor for the increase in prevalence of wheeze in 13- to 14-year-old schoolchildren in Guangzhou city, China. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013;43:1171–1179. - PubMed
-
- Mueller GA, Benjamin DC, Rule GS. Tertiary structure of the major house dust mite allergen Der p 2: sequential and structural homologies. Biochemistry. 1998;37:12707–12714. - PubMed
-
- Thomas WR, Smith WA, Hales BJ. The allergenic specificities of the house dust mite. Chang Gung Med J. 2004;27:563–569. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
