Chatty maps: constructing sound maps of urban areas from social media data
- PMID: 27069661
- PMCID: PMC4821272
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.150690
Chatty maps: constructing sound maps of urban areas from social media data
Abstract
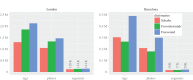
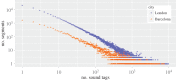
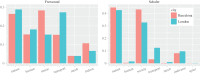
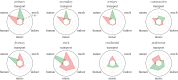
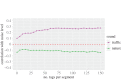
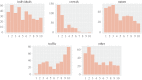
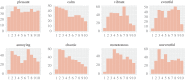
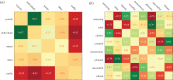
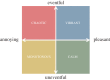
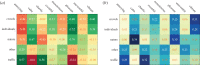
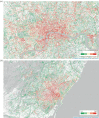
Urban sound has a huge influence over how we perceive places. Yet, city planning is concerned mainly with noise, simply because annoying sounds come to the attention of city officials in the form of complaints, whereas general urban sounds do not come to the attention as they cannot be easily captured at city scale. To capture both unpleasant and pleasant sounds, we applied a new methodology that relies on tagging information of georeferenced pictures to the cities of London and Barcelona. To begin with, we compiled the first urban sound dictionary and compared it with the one produced by collating insights from the literature: ours was experimentally more valid (if correlated with official noise pollution levels) and offered a wider geographical coverage. From picture tags, we then studied the relationship between soundscapes and emotions. We learned that streets with music sounds were associated with strong emotions of joy or sadness, whereas those with human sounds were associated with joy or surprise. Finally, we studied the relationship between soundscapes and people's perceptions and, in so doing, we were able to map which areas are chaotic, monotonous, calm and exciting. Those insights promise to inform the creation of restorative experiences in our increasingly urbanized world.
Keywords: mapping; soundscape; urban informatics.
Figures







References
-
- Halonen J. et al. 2015. Road traffic noise is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality and all-cause mortality in London. Eur. Heart J. 36, 2653–2661. (doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv216) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stansfeld SA. et al. 2005. Aircraft and road traffic noise and children's cognition and health: a cross-national study. Lancet 365, 1942–1949. (doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66660-3) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Kempen E, Babisch W. 2012. The quantitative relationship between road traffic noise and hypertension: a meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 30, 1075–1086. (doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e328352ac54) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann B. et al. 2006. Residence close to high traffic and prevalence of coronary heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 27, 2696–2702. (doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl278) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Selander J, Nilsson ME, Bluhm G, Rosenlund M, Lindqvist M, Nise G, Pershagena G. 2009. Long-term exposure to road traffic noise and myocardial infarction. Epidemiology 20, 272–279. (doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e31819463bd) - DOI - PubMed
