Pine polyphenols from Pinus koraiensis prevent injuries induced by gamma radiation in mice
- PMID: 27069807
- PMCID: PMC4824883
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1870
Pine polyphenols from Pinus koraiensis prevent injuries induced by gamma radiation in mice
Abstract
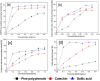
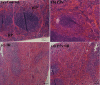
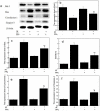
Pine polyphenols (PPs) are bioactive dietary constituents that enhance health and help prevent diseases through antioxidants. Antioxidants reduce the level of oxidative damages caused by ionizing radiation (IR). The main purpose of this paper is to study the protective effect of PPs on peripheral blood, liver and spleen injuries in mice induced by IR. ICR (Institute of Cancer Research) male mice were administered orally with PPs (200 mg/kg b.wt.) once daily for 14 consecutive days prior to 7 Gy γ-radiations. PPs showed strong antioxidant activities. PPs significantly increased white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets counts. PPs also significantly reduced lipid peroxidation and increased the activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidases, and the level of glutathione. PPs reduced the spleen morphologic injury. In addition, PPs inhibited mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathways in splenocytes induced by IR. These results indicate that PPs are radioprotective promising reagents.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Apoptosis; Pine polyphenols; Redox; γ-radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective Effects on 60Co-γ Radiation Damage of Pine Cone Polyphenols from Pinus koraiensis-Loaded Chitosan Microspheres In Vivo.Molecules. 2018 Jun 8;23(6):1392. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061392. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29890658 Free PMC article.
-
Study on antitumor, antioxidant and immunoregulatory activities of the purified polyphenols from pinecone of Pinus koraiensis on tumor-bearing S180 mice in vivo.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Jan;94(Pt A):735-744. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.071. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 27793678
-
Preparation optimization and protective effect on 60Co-γ radiation damage of Pinus koraiensis pinecone polyphenols microspheres.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Jul 1;113:583-591. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.131. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29501841
-
Palliative effects of lutein intervention in gamma-radiation-induced cellular damages in Swiss albino mice.Indian J Pharmacol. 2017 Jan-Feb;49(1):26-33. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.201013. Indian J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28458419 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration in the glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and lipid peroxidation by ascorbic acid in the skin of mice exposed to fractionated gamma radiation.Clin Chim Acta. 2003 Jun;332(1-2):111-21. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(03)00132-3. Clin Chim Acta. 2003. PMID: 12763288
Cited by
-
Protective Effects on 60Co-γ Radiation Damage of Pine Cone Polyphenols from Pinus koraiensis-Loaded Chitosan Microspheres In Vivo.Molecules. 2018 Jun 8;23(6):1392. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061392. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29890658 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Bioassay-guided Isolation of Radioprotective Fractions from Extracts of Pinus koraiensis Bark.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Oct-Dec;13(52):712-718. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_409_16. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 29200738 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of radiation-induced liver damage by p-coumaric acid in mice.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 15;31(10):1315-1323. doi: 10.1007/s10068-022-01118-8. eCollection 2022 Sep. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35992325 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Obesity Effect of Pine Needle Extract on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Plants (Basel). 2021 Apr 21;10(5):837. doi: 10.3390/plants10050837. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919440 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison in antioxidant and antitumor activities of pine polyphenols and its seven biotransformation extracts by fungi.PeerJ. 2017 May 23;5:e3264. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3264. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28560092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arora R. Herbal radiomodulators: applications in medicine, homeland defence and space. CABI Publishing; Wallingforrd: 2008. pp. 175–194.
-
- Biswas AK, Chatli MK, Sahoo J. Antioxidant potential of curry (Murraya koenigii L.) and mint (Mentha spicata) leaf extracts and their effect on colour and oxidative stability of raw ground pork meat during refrigeration storage. Food Chemistry. 2012;133:467–472. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

