Matrix Hyaluronan Promotes Specific MicroRNA Upregulation Leading to Drug Resistance and Tumor Progression
- PMID: 27070574
- PMCID: PMC4848973
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17040517
Matrix Hyaluronan Promotes Specific MicroRNA Upregulation Leading to Drug Resistance and Tumor Progression
Abstract
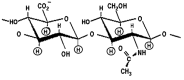
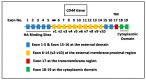
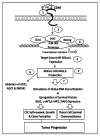
Solid tumor invasion, metastasis and therapeutic drug resistance are the common causes for serious morbidity and cancer recurrence in patients. A number of research studies have searched for malignancy-related biomarkers and drug targets that are closely linked to tumor cell properties. One of the candidates is matrix hyaluronan (HA), which is known as one of the major extracellular matrix (ECM) components. HA serves as a physiological ligand for surface CD44 molecule and also functions as a bio-regulator. The binding of HA to CD44 has been shown to stimulate concomitant activation of a number of oncogenic pathways and abnormal cellular processes in cancer cells and cancer stem cells (CSCs). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) belong to a class of small RNAs containing ~20-25 nucleotides and are known to promote aberrant cellular functions in cancer cells. In this article, I have focused on the role of HA interaction with CD44 and several important signaling molecules in the regulation of unique miRNAs (e.g., miR-21, miR-302 and miR-10b) and their downstream targets leading to multiple tumor cell-specific functions (e.g., tumor cell growth, drug resistance and metastasis) and cancer progression. This new knowledge could provide the groundwork necessary for establishing new tumor markers and developing important, novel drugs targeted against HA/CD44-associated tumor progression, which can be utilized in the therapeutic treatment of metastatic cancer patients.
Keywords: CD44; cancer stem cells (CSCs); chemoresistance; hyaluronan (HA); microRNA (miRNA); signaling; tumor progression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of Histone Methyltransferase, DOT1L, by Matrix Hyaluronan Promotes MicroRNA-10 Expression Leading to Tumor Cell Invasion and Chemoresistance in Cancer Stem Cells from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 13;291(20):10571-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.700021. Epub 2016 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27002147 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Matrix Hyaluronan-Mediated CD44 Signaling, Epigenetic Regulation and Chemoresistance in Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 24;18(9):1849. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091849. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28837080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes oncogenic signaling, microRNA functions, chemoresistance, and radiation resistance in cancer stem cells leading to tumor progression.Adv Cancer Res. 2014;123:255-75. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800092-2.00010-1. Adv Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25081533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes microRNA signaling and RhoGTPase activation leading to tumor progression.Small GTPases. 2012 Jan-Mar;3(1):53-9. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.19110. Small GTPases. 2012. PMID: 22714418 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Hyaluronan-CD44 Interaction Activates MicroRNA and LncRNA Signaling Associated With Chemoresistance, Invasion, and Tumor Progression.Front Oncol. 2019 Jun 21;9:492. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00492. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31293964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor Microenvironment: A Niche for Cancer Stem Cell Immunotherapy.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 Jan;20(1):3-24. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10639-6. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 37861969 Review.
-
Collagen- and hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels and their biomedical applications.Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2021 Oct;146:100641. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2021.100641. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2021. PMID: 34483486 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Chemoresistance: 3D Extracellular Matrices as Accomplices.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 20;19(10):2861. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102861. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30241395 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated silencing of CD44: unveiling the role of hyaluronic acid-mediated interactions in cancer drug resistance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 May;397(5):2849-2876. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02840-8. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37991544 Review.
-
MicroRNA-21-5p targeting PDCD4 suppresses apoptosis via regulating the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway in tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Nov;18(5):3543-3551. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7970. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31602231 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

