The N-Terminal GYPSY Motif Is Required for Pilin-Specific Sortase SrtC1 Functionality in Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strain GG
- PMID: 27070897
- PMCID: PMC4829219
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153373
The N-Terminal GYPSY Motif Is Required for Pilin-Specific Sortase SrtC1 Functionality in Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strain GG
Abstract
Predominantly identified in pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria, sortase-dependent pili are also found in commensal species, such as the probiotic-marketed strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Pili are typically associated with host colonization, immune signalling and biofilm formation. Comparative analysis of the N-terminal domains of pilin-specific sortases from various piliated Gram-positive bacteria identified a conserved motif, called GYPSY, within the signal sequence. We investigated the function and role of the GYPSY residues by directed mutagenesis in homologous (rod-shaped) and heterologous (coccoid-shaped) expression systems for pilus formation. Substitutions of some of the GYPSY residues, and more specifically the proline residue, were found to have a direct impact on the degree of piliation of Lb. rhamnosus GG. The present findings uncover a new signalling element involved in the functionality of pilin-specific sortases controlling the pilus biogenesis of Lb. rhamnosus GG and related piliated Gram-positive species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





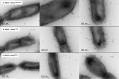
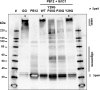


References
-
- Vanier G, Sekizaki T, Dominguez-Punaro MC, Esgleas M, Osaki M, Takamatsu D, et al. (2008) Disruption of srtA gene in Streptococcus suis results in decreased interactions with endothelial cells and extracellular matrix proteins. Vet Microbiol 127: 417–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

