Improving fascin inhibitors to block tumor cell migration and metastasis
- PMID: 27071719
- PMCID: PMC5423182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2016.03.006
Improving fascin inhibitors to block tumor cell migration and metastasis
Abstract
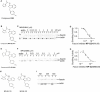
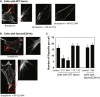
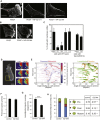
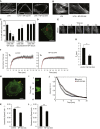
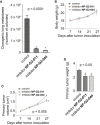
Tumor metastasis is the major cause of mortality of cancer patients, being responsible for ∼90% of all cancer deaths. One of the key steps during tumor metastasis is tumor cell migration which requires actin cytoskeletal reorganization. Among the critical actin cytoskeletal protrusion structures are antenna-like filopodia. Fascin protein is the main actin-bundling protein in filopodia. Here we report the development of fascin-specific small-molecules that inhibit the interaction between fascin and actin. These inhibitors block the in vitro actin-binding and actin-bundling activities of fascin, tumor cell migration and tumor metastasis in mouse models. Mechanistically, these inhibitors likely occupy one of the actin-binding sites, reduce the binding of actin filaments, and thus lead to the inhibition of the bundling activity of fascin. At the cellular level, these inhibitors impair actin cytoskeletal reorganization. Our data indicate that target-specific anti-fascin agents will have great potential for treating metastatic tumors.
Keywords: Fascin; Inhibitors; Metastasis.
Copyright © 2016 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, J.C. , 2004. Roles of fascin in cell adhesion and motility. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16, 590–596. - PubMed
-
- Aznavoorian, S. , Murphy, A.N. , Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. , Liotta, L.A. , 1993. Molecular aspects of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer. 71, 1368–1383. - PubMed
-
- Bentley, D. , Toroian-Raymond, A. , 1986. Disoriented pathfinding by pioneer neurone growth cones deprived of filopodia by cytochalasin treatment. Nature. 323, 712–715. - PubMed
-
- Bryan, J. , Kane, R.E. , 1978. Separation and interaction of the major components of sea urchin actin gel. J. Mol. Biol. 125, 207–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

