Systemic administration of an HIV-1 broadly neutralizing dimeric IgA yields mucosal secretory IgA and virus neutralization
- PMID: 27072605
- PMCID: PMC5063654
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2016.32
Systemic administration of an HIV-1 broadly neutralizing dimeric IgA yields mucosal secretory IgA and virus neutralization
Abstract
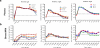
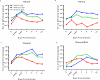
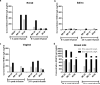
We investigated the mucosal distribution and neutralization potency of rhesus recombinant versions of the HIV-specific, broadly neutralizing antibody b12 (RhB12) following intravenous administration to lactating rhesus monkeys. IgG and dimeric IgA (dIgA) administration resulted in high plasma concentrations of broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb), but the monomeric IgA (mIgA) was rapidly cleared from the systemic compartment. Interestingly, differences in the distribution of the RhB12 isoform were observed between the mucosal compartments. The peak concentration of RhB12 IgG was higher than dIgA in saliva, rectal, and vaginal secretions, but the bnAb concentration in milk was one to two logs higher after dIgA administration than with IgG or mIgA infusion. Neutralization was observed in plasma of all animals, but only those infused with RhB12 dIgA showed moderate levels of virus neutralization in milk. Remarkably, virus-specific secretory IgA was detected in mucosal compartments following dIgA administration. The high milk RhB12 dIgA concentration suggests that passive immunization with dIgA could be more effective than IgG to inhibit virus in breast milk.
Figures

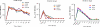
Similar articles
-
Rare Detection of Antiviral Functions of Polyclonal IgA Isolated from Plasma and Breast Milk Compartments in Women Chronically Infected with HIV-1.J Virol. 2019 Mar 21;93(7):e02084-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02084-18. Print 2019 Apr 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30700599 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization Takes Precedence Over IgG or IgA Isotype-related Functions in Mucosal HIV-1 Antibody-mediated Protection.EBioMedicine. 2016 Dec;14:97-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.11.024. Epub 2016 Nov 21. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27919754 Free PMC article.
-
Combined HIV-1 Envelope Systemic and Mucosal Immunization of Lactating Rhesus Monkeys Induces a Robust Immunoglobulin A Isotype B Cell Response in Breast Milk.J Virol. 2016 Apr 29;90(10):4951-4965. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00335-16. Print 2016 May 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26937027 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral immune responses to HIV in the mucosal secretions and sera of HIV-infected women.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014 Jun;71(6):600-7. doi: 10.1111/aji.12203. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24494997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multifaceted Nature of Immunoglobulin A and Its Complex Role in HIV.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2018 Sep;34(9):727-738. doi: 10.1089/AID.2018.0099. Epub 2018 Aug 27. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2018. PMID: 30056749 Review.
Cited by
-
The secretory IgA (sIgA) response in human milk against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike is highly durable and neutralizing for at least 1 year of lactation post-infection.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 26:2023.05.19.23290192. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.19.23290192. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Breastfeed Med. 2023 Aug;18(8):602-611. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2023.0117. PMID: 37293109 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Secretory IgA Response in Human Milk Against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Is Highly Durable and Neutralizing for At Least 1 Year of Lactation Postinfection.Breastfeed Med. 2023 Aug;18(8):602-611. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2023.0117. Breastfeed Med. 2023. PMID: 37615565 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Safety of Breastfeeding in Infants Born to Infected Mothers.Front Pediatr. 2021 Dec 9;9:738263. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.738263. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34956971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 Entry and Prospects for Protecting against Infection.Microorganisms. 2021 Jan 22;9(2):228. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020228. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33499233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Similar Epitope Specificities of IgG and IgA Antibodies Elicited by Ad26 Vector Prime, Env Protein Boost Immunizations in Rhesus Monkeys.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00537-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00537-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29793950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS . Progress report on the global plan towards the elimination of new HIV infections among children vy 2015 and keeping their mothers alive. 2014.
-
- Fowler MG, Coovadia H, Herron CM, Maldonado Y, Chipato T, Moodley D, et al. Efficacy and safety of an extended nevirapine regimen in infants of breastfeeding mothers with HIV-1 infection for prevention of HIV-1 transmission (HPTN 046): 18-month results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2014;65:366–374. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kesho Bora Study G, de Vincenzi I. Triple antiretroviral compared with zidovudine and single-dose nevirapine prophylaxis during pregnancy and breastfeeding for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 (Kesho Bora study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;11:171–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

