Elevated expression of flotillin-1 is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in early-stage cervical cancer
- PMID: 27073721
- PMCID: PMC4759395
Elevated expression of flotillin-1 is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in early-stage cervical cancer
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Elevated expression of flotillin-1 is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in early-stage cervical cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Nov 15;11(11):5759-5760. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34873493 Free PMC article.
Abstract
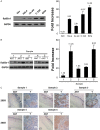
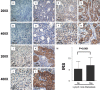
Accumulating evidence has revealed that the expression of the lipid raft protein flotillin-1 is elevated in various human cancers, but the role flotillin-1 plays in the carcinogenesis of cervical cancer remains unclear. The expression profile of flotillin-1 was assayed using real-time PCR, western blotting, and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining in cervical cancer cell lines and cancer tissues with paired adjacent noncancerous cervical tissues. The expression of flotillin-1 protein was detected by IHC staining in a large cohort of 308 paraffin-embedded cervical cancer tissues. Ectopic expression and the short hairpin RNA interference approach were employed to determine the role of flotillin-1 in cervical cancer cell metastasis and the possible mechanism involved. Flotillin-1 expression protein and mRNA were significantly upregulated in cervical cancer cell lines and cancer tissues; elevated expression of flotillin-1 protein in early-stage cervical cancer was significantly associated with pelvic lymph node metastasis (P < 0.001), and was an independent predictive factor of poor overall survival. Moreover, flotillin-1 up- and downregulation remarkably affected cervical cancer cell motility and invasion, respectively, through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) regulated by the Wnt/β-catenin and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways. Our results suggest that flotillin-1 facilitates cervical cancer cell metastasis through Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB pathway-regulated EMT and that the flotillin-1 expression profile serves not only as novel predictor of pelvic lymph node metastasis, but also as neoteric risk factor for patients with early-stage cervical cancer.
Keywords: EMT; Flotillin-1; Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB pathways; cervical cancer; lymph node metastasis; prognosis.
Figures



References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Barakat R, Berchuck A, Markman M, Randall ME. Principles and Practice of Gynecologic Oncology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013.
-
- Benedetti Panici P, Basile S, Angioli R. Pelvic and aortic lymphadenectomy in cervical cancer: the standardization of surgical procedure and its clinical impact. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;113:284–290. - PubMed
-
- Pike LJ. Rafts defined: a report on the Keystone Symposium on Lipid Rafts and Cell Function. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:1597–1598. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
