Age-dependent modulation of vascular niches for haematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 27074508
- PMCID: PMC5035541
- DOI: 10.1038/nature17638
Age-dependent modulation of vascular niches for haematopoietic stem cells
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Age-dependent modulation of vascular niches for haematopoietic stem cells.Nature. 2016 Nov 10;539(7628):314. doi: 10.1038/nature19782. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27626373 No abstract available.
Abstract
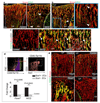
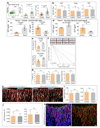
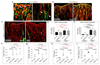
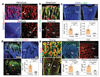
Blood vessels define local microenvironments in the skeletal system, play crucial roles in osteogenesis and provide niches for haematopoietic stem cells. The properties of niche-forming vessels and their changes in the ageing organism remain incompletely understood. Here we show that Notch signalling in endothelial cells leads to the expansion of haematopoietic stem cell niches in bone, which involves increases in CD31-positive capillaries and platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β (PDGFRβ)-positive perivascular cells, arteriole formation and elevated levels of cellular stem cell factor. Although endothelial hypoxia-inducible factor signalling promotes some of these changes, it fails to enhance vascular niche function because of a lack of arterialization and expansion of PDGFRβ-positive cells. In ageing mice, niche-forming vessels in the skeletal system are strongly reduced but can be restored by activation of endothelial Notch signalling. These findings indicate that vascular niches for haematopoietic stem cells are part of complex, age-dependent microenvironments involving multiple cell populations and vessel subtypes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not declare competing financial interests.
Figures










References
-
- Kiel MJ, et al. SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell. 2005;121:1109–1121. - PubMed

