STAT3 and NF-κB cooperatively control in vitro spontaneous apoptosis and poor chemo-responsiveness in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 27074565
- PMCID: PMC5077994
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8672
STAT3 and NF-κB cooperatively control in vitro spontaneous apoptosis and poor chemo-responsiveness in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
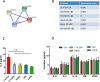
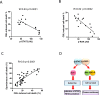
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is an adult disease characterized by in vivo accumulation of mature CD5/CD19/CD23 triple positive B cells and is currently incurable. CLL cells undergo spontaneous apoptosis in response to in vitro cell culture condition but the underlying mechanism is unclear. We hypothesize that the sensitivity of CLL cells to spontaneous apoptosis may be associated with the constitutive activities of transcription factors STAT3 and/or NF-κB. We now show that the sensitivity of fresh CLL cells to spontaneous apoptosis is highly variable among different patients during 48 hours' cell culture and inversely correlated with in vivo constitutively activated STAT3 and NF-κB (p < 0.001). Both activated STAT3 and NF-κB maintain the levels of anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1/Bcl-xL and autocrine IL-6 production. CLL cells with higher susceptibility to in vitro spontaneous apoptosis show the greatest chemosensitivity (p < 0.001), which is reflected clinically as achieving a complete response (CR) (p < 0.001), longer lymphocyte doubling times (p < 0.01), time to first treatment (p < 0.01), and progression free survival (p < 0.05). Our data suggest that the sensitivity of CLL cells to in vitro spontaneous apoptosis is co-regulated by constitutively activated STAT3 and NF-κB and reflects the in vivo chemo-responsiveness and clinical outcomes.
Keywords: NF-kB; STAT3; chronic lymphocytic leukemia; prognosis; spontaneous apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Caligaris-Cappio F, Ghia P. Novel insights in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Are we getting closer to understanding the pathogenesis of the disease? J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4497–4503. - PubMed
-
- Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:804–815. - PubMed
-
- Collins RJ, Verschuer LA, Harmon BV, Prentice RL, Pope JH, Kerr JF. Spontaneous programmed death (apoptosis) of b-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells following their culture in vitro. Br J Haematol. 1989;71:343–350. - PubMed
-
- Witkowska M, Nowak W, Cebula-Obrzut B, Majchrzak A, Medra A, Robak T, Smolewski P. Spontaneous in vitro apoptosis of de novo chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells correlates with risk of the disease progression. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2014;86:410–417. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

