Revealing Assembly of a Pore-Forming Complex Using Single-Cell Kinetic Analysis and Modeling
- PMID: 27074682
- PMCID: PMC4833779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.02.035
Revealing Assembly of a Pore-Forming Complex Using Single-Cell Kinetic Analysis and Modeling
Abstract
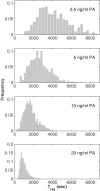
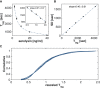
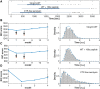
Many biological processes depend on the sequential assembly of protein complexes. However, studying the kinetics of such processes by direct methods is often not feasible. As an important class of such protein complexes, pore-forming toxins start their journey as soluble monomeric proteins, and oligomerize into transmembrane complexes to eventually form pores in the target cell membrane. Here, we monitored pore formation kinetics for the well-characterized bacterial pore-forming toxin aerolysin in single cells in real time to determine the lag times leading to the formation of the first functional pores per cell. Probabilistic modeling of these lag times revealed that one slow and seven equally fast rate-limiting reactions best explain the overall pore formation kinetics. The model predicted that monomer activation is the rate-limiting step for the entire pore formation process. We hypothesized that this could be through release of a propeptide and indeed found that peptide removal abolished these steps. This study illustrates how stochasticity in the kinetics of a complex process can be exploited to identify rate-limiting mechanisms underlying multistep biomolecular assembly pathways.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Minton A.P. Implications of macromolecular crowding for protein assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000;10:34–39. - PubMed
-
- Morris A.M., Watzky M.A., Finke R.G. Protein aggregation kinetics, mechanism, and curve-fitting: a review of the literature. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1794:375–397. - PubMed
-
- Karsenti E., Nédélec F., Surrey T. Modelling microtubule patterns. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006;8:1204–1211. - PubMed
-
- Bischofberger M., Gonzalez M.R., van der Goot F.G. Membrane injury by pore-forming proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009;21:589–595. - PubMed
-
- Iacovache I., van der Goot F.G., Pernot L. Pore formation: an ancient yet complex form of attack. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008;1778:1611–1623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

