The effects of antibiotics on the microbiome throughout development and alternative approaches for therapeutic modulation
- PMID: 27074706
- PMCID: PMC4831151
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-016-0294-z
The effects of antibiotics on the microbiome throughout development and alternative approaches for therapeutic modulation
Abstract
The widespread use of antibiotics in the past 80 years has saved millions of human lives, facilitated technological progress and killed incalculable numbers of microbes, both pathogenic and commensal. Human-associated microbes perform an array of important functions, and we are now just beginning to understand the ways in which antibiotics have reshaped their ecology and the functional consequences of these changes. Mounting evidence shows that antibiotics influence the function of the immune system, our ability to resist infection, and our capacity for processing food. Therefore, it is now more important than ever to revisit how we use antibiotics. This review summarizes current research on the short-term and long-term consequences of antibiotic use on the human microbiome, from early life to adulthood, and its effect on diseases such as malnutrition, obesity, diabetes, and Clostridium difficile infection. Motivated by the consequences of inappropriate antibiotic use, we explore recent progress in the development of antivirulence approaches for resisting infection while minimizing resistance to therapy. We close the article by discussing probiotics and fecal microbiota transplants, which promise to restore the microbiota after damage of the microbiome. Together, the results of studies in this field emphasize the importance of developing a mechanistic understanding of gut ecology to enable the development of new therapeutic strategies and to rationally limit the use of antibiotic compounds.
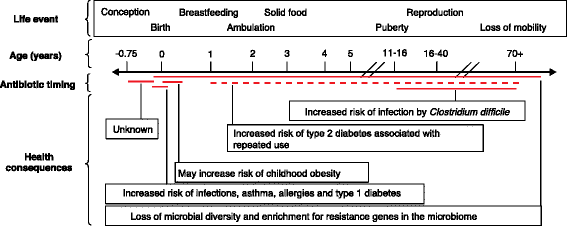
Figures
References
-
- Review on Antimibrobial Resistance. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. 2014. http://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20-%20Tac.... Accessed 5 Apr 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

