Qishen Yiqi Drop Pill improves cardiac function after myocardial ischemia
- PMID: 27075394
- PMCID: PMC4830957
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24383
Qishen Yiqi Drop Pill improves cardiac function after myocardial ischemia
Abstract
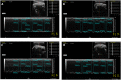
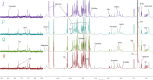
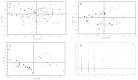
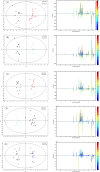
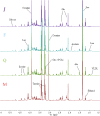
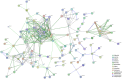
Myocardial ischemia (MI) is one of the leading causes of death, while Qishen Yiqi Drop Pill (QYDP) is a representative traditional Chinese medicine to treat this disease. Unveiling the pharmacological mechanism of QYDP will provide a great opportunity to promote the development of novel drugs to treat MI. 64 male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided into four groups: MI model group, sham operation group, QYDP treatment group and Fosinopril treatment group. Echocardiography results showed that QYDP exhibited significantly larger LV end-diastolic dimension (LVEDd) and LV end-systolic dimension (LVEDs), compared with the MI model group, indicating the improved cardiac function by QYDP. (1)H-NMR based metabonomics further identify 9 significantly changed metabolites in the QYDP treatment group, and the QYDP-related proteins based on the protein-metabolite interaction networks and the corresponding pathways were explored, involving the pyruvate metabolism pathway, the retinol metabolism pathway, the tyrosine metabolism pathway and the purine metabolism pathway, suggesting that QYDP was closely associated with blood circulation. ELISA tests were further employed to identify NO synthase (iNOS) and cathepsin K (CTSK) in the networks. For the first time, our work combined experimental and computational methods to study the mechanism of the formula of traditional Chinese medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Qishen Yiqi Dropping Pills Ameliorates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice via Enhancement of Cardiac Angiogenesis.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Apr 3;25:2435-2444. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915194. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30943187 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of Qishen Yiqi Dropping Pill on myocardial injury induced by chronic hypoxia in rats.Chin J Nat Med. 2015 Oct;13(10):776-80. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(15)30078-9. Chin J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26481378
-
QishenYiqi Dripping Pill Improves Heart Failure by Up-Regulation of β2-Adrenergic Receptor Expression.J Heart Valve Dis. 2017 Mar;26(2):193-199. J Heart Valve Dis. 2017. PMID: 28820549
-
A stepwise integrated strategy to explore quality markers of Qishen Yiqi dripping pills against myocardial ischemia.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156182. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156182. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39488103
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
Cited by
-
Salvia miltiorrhiza and the Volatile of Dalbergia odorifera Attenuate Chronic Myocardial Ischemia Injury in a Pig Model: A Metabonomic Approach for the Mechanism Study.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 28;2021:8840896. doi: 10.1155/2021/8840896. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34007406 Free PMC article.
-
QiShenYiQi pill improves the reparative myocardial fibrosis by regulating autophagy.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(19):11283-11293. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15695. Epub 2020 Sep 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32881330 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective effects and underlying mechanism of Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza and Lignum Dalbergia odorifera in a pig chronic myocardial ischemia model.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Nov;42(5):2628-2640. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3844. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30226574 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroprotective Effects and Multitarget Mechanisms of Fu Yuan Capsule in a Rat Osteoarthritis Model.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:8985623. doi: 10.1155/2017/8985623. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28167976 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Protective Mechanism of NO, H2S, and H2 in Myocardial Ischemic Injury.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Oct 30;7:588206. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.588206. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 33195476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mann D. L., Zipes D. P., Libby P., Bonow R. O. & Braunwald E. Approach to the patient with chest pain. In: Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 10th ed. Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders Elsevier, (2014).
-
- Lu Z. Q., Zhang Y. J., Cui G. Z., Zhuang P. W. & Zhang J. B. Progress in preparation methodology of animal models of myocardial ischemia. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 28, 1053–1057 (2012).
-
- Shimokawa H. & Yasuda S. Myocardial ischemia: current concepts and future perspectives. J. Cardiol. 52, 67–78 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Fang L., Qian X., Ting Z., Fang H. & Lintao H. Metabonomic analysis of allium macrostemon bunge as a treatment for acute myocardial ischemia in rats. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 88, 225–234 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Sabatine M. S. et al. Metabolomic identification of novel biomarkers of myocardial ischemia. Circulation 112, 3868–3875 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

