Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx)-induced abnormalities of nucleic acid metabolism revealed by (1)H-NMR-based metabonomics
- PMID: 27075403
- PMCID: PMC4830998
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24430
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx)-induced abnormalities of nucleic acid metabolism revealed by (1)H-NMR-based metabonomics
Abstract
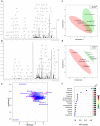
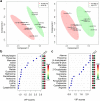
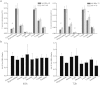
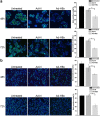
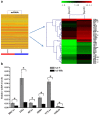
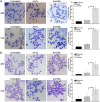
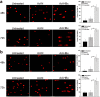
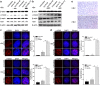
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) plays an important role in HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis; however, mechanisms underlying HBx-mediated carcinogenesis remain unclear. In this study, an NMR-based metabolomics approach was applied to systematically investigate the effects of HBx on cell metabolism. EdU incorporation assay was conducted to examine the effects of HBx on DNA synthesis, an important feature of nucleic acid metabolism. The results revealed that HBx disrupted metabolism of glucose, lipids, and amino acids, especially nucleic acids. To understand the potential mechanism of HBx-induced abnormalities of nucleic acid metabolism, gene expression profiles of HepG2 cells expressing HBx were investigated. The results showed that 29 genes involved in DNA damage and DNA repair were differentially expressed in HBx-expressing HepG2 cells. HBx-induced DNA damage was further demonstrated by karyotyping, comet assay, Western blotting, immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry analyses. Many studies have previously reported that DNA damage can induce abnormalities of nucleic acid metabolism. Thus, our results implied that HBx initially induces DNA damage, and then disrupts nucleic acid metabolism, which in turn blocks DNA repair and induces the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These findings further contribute to our understanding of the occurrence of HCC.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

