Protocol for evaluating the effects of a therapeutic foot exercise program on injury incidence, foot functionality and biomechanics in long-distance runners: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27075480
- PMCID: PMC4831173
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-1016-9
Protocol for evaluating the effects of a therapeutic foot exercise program on injury incidence, foot functionality and biomechanics in long-distance runners: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Overall performance, particularly in a very popular sports activity such as running, is typically influenced by the status of the musculoskeletal system and the level of training and conditioning of the biological structures. Any change in the musculoskeletal system's biomechanics, especially in the feet and ankles, will strongly influence the biomechanics of runners, possibly predisposing them to injuries. A thorough understanding of the effects of a therapeutic approach focused on feet biomechanics, on strength and functionality of lower limb muscles will contribute to the adoption of more effective therapeutic and preventive strategies for runners.
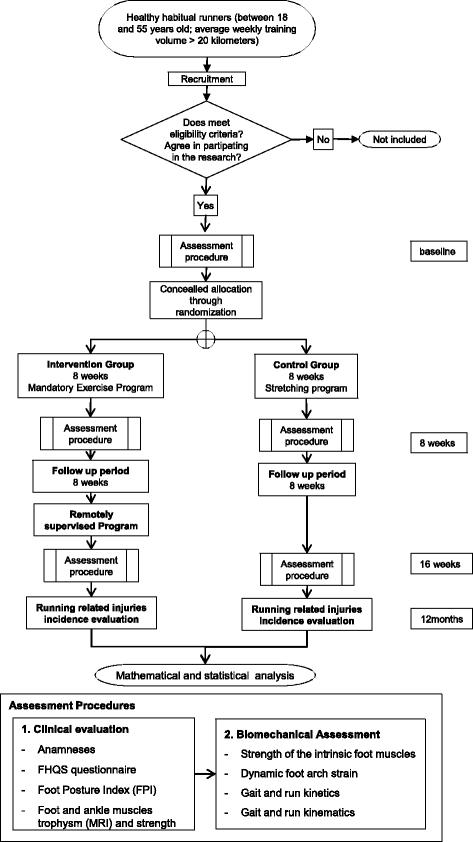
Methods/design: A randomized, prospective controlled and parallel trial with blind assessment is designed to study the effects of a "ground-up" therapeutic approach focused on the foot-ankle complex as it relates to the incidence of running-related injuries in the lower limbs. One hundred and eleven (111) healthy long-distance runners will be randomly assigned to either a control (CG) or intervention (IG) group. IG runners will participate in a therapeutic exercise protocol for the foot-ankle for 8 weeks, with 1 directly supervised session and 3 remotely supervised sessions per week. After the 8-week period, IG runners will keep exercising for the remaining 10 months of the study, supervised only by web-enabled software three times a week. At baseline, 2 months, 4 months and 12 months, all runners will be assessed for running-related injuries (primary outcome), time for the occurrence of the first injury, foot health and functionality, muscle trophism, intrinsic foot muscle strength, dynamic foot arch strain and lower-limb biomechanics during walking and running (secondary outcomes).
Discussion: This is the first randomized clinical trial protocol to assess the effect of an exercise protocol that was designed specifically for the foot-and-ankle complex on running-related injuries to the lower limbs of long-distance runners. We intend to show that the proposed protocol is an innovative and effective approach to decreasing the incidence of injuries. We also expect a lengthening in the time of occurrence of the first injury, an improvement in foot function, an increase in foot muscle mass and strength and beneficial biomechanical changes while running and walking after a year of exercising.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier NCT02306148 (November 28, 2014) under the name "Effects of Foot Strengthening on the Prevalence of Injuries in Long Distance Runners". Committee of Ethics in Research of the School of Medicine of the University of Sao Paulo (18/03/2015, Protocol # 031/15).
Keywords: Biomechanics; Exercise therapy; Foot; Running; Sports injuries.
References
-
- Haskell WL, Lee I-M, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, Macera CA, Heath GW, Thompson PD, Bauman A. Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39:1423–34. doi: 10.1249/mss.0b013e3180616b27. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical