Salidroside alleviates oxidative stress in the liver with non- alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats
- PMID: 27075663
- PMCID: PMC4831194
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-016-0059-8
Salidroside alleviates oxidative stress in the liver with non- alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is characterized by fat accumulation in the hepatocyte, inflammation, liver cell injury, and varying degrees of fibrosis, and can lead to oxidative stress in liver. Here, we investigated whether Salidroside, a natural phenolic antioxidant product, can protect rat from liver injury during NASH.
Methods: NASH model was established by feeding the male SD rats with high-fat and high-cholesterol diet for 14 weeks. Four groups of male SD rats including, normal diet control group, NASH model group, and Salidroside treatment group with150mg/kg and 300 mg/kg respectively, were studied. Salidroside was given by oral administration to NASH in rats from 9 weeks to 14 weeks. At the end of 14 weeks, liver and serum were harvested, and the liver injury, oxidative stress and histological features were evaluated.
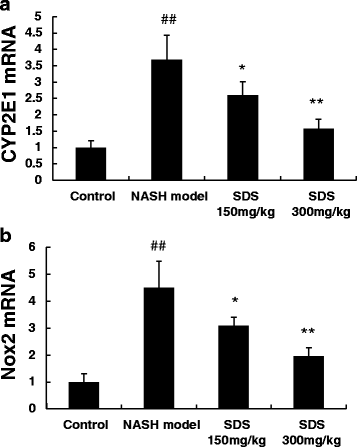
Results: NASH rats exhibited significant increases in the following parameters as compared to normal diet control rats: fat droplets with foci of inflammatory cell infiltration in the liver. ALT, AST in serum and TG, TC in hepatocyte elevated. Oxidative responsive genes including CYP2E1 and Nox2 increased. Additionally, NASH model decreased antioxidant enzymes SOD, GSH, GPX, and CAT in the liver due to their rapid depletion after battling against oxidative stress. Compared to NASH model group, treatment rats with Salidroside effectively reduced lipid accumulation, inhibited liver injury in a does-dependent manner. Salidroside treatment restored antioxidant enzyme levels, inhibited expression of CYP2E1 and Nox2 mRNA in liver, which prevented the initial step of generating free radicals from NASH.
Conclusion: The data presented here show that oral administration of Salidroside prevented liver injury in the NASH model, likely through exerting antioxidant actions to suppress oxidative stress and the free radical-generating CYP2E1 enzyme, Nox2 in liver.
Keywords: CYP2E1; Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; Nox2; Oxidative stress; Salidroside.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Salidroside on Lead Acetate-induced Oxidative Stress and Hepatotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019 Oct;191(2):426-434. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-1635-8. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019. PMID: 30666592
-
Antioxidant properties of proanthocyanidins attenuate carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced steatosis and liver injury in rats via CYP2E1 regulation.J Med Food. 2014 Jun;17(6):663-9. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2013.2834. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Med Food. 2014. PMID: 24712752 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of lycopene on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rat.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Dec 14;22(46):10180-10188. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10180. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 28028366 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism Analysis and Prevention of Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis].Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2015;70(3):197-204. doi: 10.1265/jjh.70.197. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26411937 Review. Japanese.
-
The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cytochrome P-450 2E1 in the generation of carcinogenic etheno-DNA adducts.Redox Biol. 2014;3:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.08.009. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Redox Biol. 2014. PMID: 25462066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Salidroside mediates apoptosis and autophagy inhibition in concanavalin A-induced liver injury.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jun;15(6):4599-4614. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6053. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29805476 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress of Natural Products with the Activity of Anti-nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(21):1894-1929. doi: 10.2174/0113895575306598240503054317. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38752645 Review.
-
Diosgenin ameliorates palmitic acid-induced lipid accumulation via AMPK/ACC/CPT-1A and SREBP-1c/FAS signaling pathways in LO2 cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Sep 13;19(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2671-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31519174 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside slows the progression of EA.hy926 cell senescence by regulating the cell cycle in an atherosclerosis model.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jan;17(1):257-263. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7872. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29115447 Free PMC article.
-
Sanguisorba officinalis L. Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis by Modulating Oxidative Stress, Fatty Acid Oxidation, and Gut Microbiota in CDAHFD-Induced Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 29;15(17):3779. doi: 10.3390/nu15173779. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB, Oh BJ. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55(7):434–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

