mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles
- PMID: 27075952
- PMCID: PMC5439223
- DOI: 10.4155/tde-2016-0006
mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Ther Deliv. 2016 Jun;7(6):411. doi: 10.4155/tde-2016-0006c1. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Ther Deliv. 2016. PMID: 27282962 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
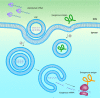
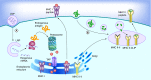
mRNA vaccines elicit a potent immune response including antibodies and cytotoxic T cells. mRNA vaccines are currently evaluated in clinical trials for cancer immunotherapy applications, but also have great potential as prophylactic vaccines. Efficient delivery of mRNA vaccines will be key for their success and translation to the clinic. Among potential nonviral vectors, lipid nanoparticles are particularly promising. Indeed, lipid nanoparticles can be synthesized with relative ease in a scalable manner, protect the mRNA against degradation, facilitate endosomal escape, can be targeted to the desired cell type by surface decoration with ligands, and as needed, can be codelivered with adjuvants.
Keywords: adjuvant; cancer immunotherapy; cationic lipid; drug delivery; lipid nanoparticle; mRNA; oligonucleotide; therapeutic vaccine; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (Grant# EB 000244). Robert Langer is a co-founder and member of the board of directors of Moderna therapeutics. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Assisted mRNA Delivery for Potent Cancer Immunotherapy.Nano Lett. 2017 Mar 8;17(3):1326-1335. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03329. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Nano Lett. 2017. PMID: 28273716 Free PMC article.
-
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines.Adv Genet. 2015;89:179-233. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Adv Genet. 2015. PMID: 25620012
-
Current landscape of mRNA technologies and delivery systems for new modality therapeutics.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Sep 10;31(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01080-z. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 39256822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA as a Transformative Technology for Vaccine Development to Control Infectious Diseases.Mol Ther. 2019 Apr 10;27(4):757-772. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.01.020. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30803823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advancements in lipid-mRNA nanoparticles as a treatment option for cancer immunotherapy.J Pharm Investig. 2022;52(4):415-426. doi: 10.1007/s40005-022-00569-9. Epub 2022 Mar 26. J Pharm Investig. 2022. PMID: 35369363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Liposomal Vaccines for Dendritic Cell Activation or Tolerance.Front Immunol. 2021 May 13;12:674048. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.674048. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclodextrins in Antiviral Therapeutics and Vaccines.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 19;13(3):409. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030409. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33808834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for HIV-1 suppression through key genes and cell therapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 29;10:1259995. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1259995. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38093984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotheranostics against COVID-19: From multivalent to immune-targeted materials.J Control Release. 2020 Dec 10;328:112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.060. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32882269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybrid Biopolymer and Lipid Nanoparticles with Improved Transfection Efficacy for mRNA.Cells. 2020 Sep 5;9(9):2034. doi: 10.3390/cells9092034. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32899484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crawford NW, Bines JE, Royle J, Buttery JP. Optimizing immunization in pediatric special risk groups. Expert Rev. Vaccines. 2011;10(2):175–186. - PubMed
-
- Liu MA. Immunologic basis of vaccine vectors. Immunity. 2010;33(4):504–515. - PubMed
-
- Hilleman MR. Recombinant vector vaccines in vaccinology. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1994;82:3–20. - PubMed
-
- Deering RP, Kommareddy S, Ulmer JB, Brito LA, Geall AJ. Nucleic acid vaccines: prospects for non-viral delivery of mRNA vaccines. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014;11(6):885–899. - PubMed
-
- Pascolo S. Vaccination with messenger RNA (mRNA) In: Bauer PDS, Hartmann PDG, editors. Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and Innate Immunity. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; Germany: 2008. pp. 221–235.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
